* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 34 - lazyoldjohn.org
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
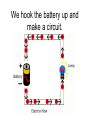
Chapter 34 Electric Current The Big Idea Electric current is related to the voltage that produces it and the resistance that opposes it. Ohm’s Law V IR Voltage equals the current times the resistance Basic Facts • We use the letter I to represent current. • Current is measured in Amperes. • Ampere or Amps or the Letter A. • We use the letter R to represent resistance. • Resistance is measured in Ohms. • Ohms or the Greek letter omega . Some Examples with V IR 1. A Battery with 10Volts is hooked up in a circuit with a resistor at 100. Calculate the current that flows through the circuit. 2. You want 1 A to flow through a resistor of 1,000. What Voltage battery will you need? 3. You have a battery with 20V. You have 3 different resistors, 10 , 100 , 1000 . Which resistor will give the largest current? Which will give the smallest current? Power! • To calculate the power used in a circuit is very similar to Ohm’s Law. V IR P IV or P I R 2 • Units for power are Watts (W). Circuit • A Complete Path We hook the battery up and make a circuit. + _ How to Draw a Battery Resistors • Resists the flow of electrons. • They get warm when they do this. • Ex. A Light bulb. Series and Parallel • Series – More then one component in a row • Parallel – One component, multiple paths. Equivalent Resistance for Series & Parallel Series Parallel Rtotal R1 R2 1 Rtotal 1 1 R1 R2 Remember Charge. • Battery has a positive (+) and a negative (-) side. • The plus (+) side does not have enough electrons. • The minus (-) side has too many electrons. • This difference is called a difference in electric potential or more commonly a Voltage. Why Electrons Move Electric current is the flow of electrons. Remember: Opposites attract. 1. Negative Charges want to move towards positive charges. 2. Electrons move freely through conductors. 3. If there are too many electrons in a place and they have a path to where there aren’t as many electrons, they will move towards that place. AC/DC • Direct Current (DC) Vs. Alternating Current (AC) Direct current stays the same while alternating current alternates with a given frequency. Capacitors • Another component of electric circuit is a capacitor. • Commonly called a cap. • They store charge and can be deadly! • The units for caps are called Farad (F). A capacitor is just two conductors separated by an insulator. Modern capacitors Old Style Cap. Transistors • Transistors are used in circuits in two ways. • 1. As an amplifier. – Transistors can amplify signals. • 2. As a switch. Transistors can act just like your light switch. – On, current flows, – Off, current does not flow.