* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Behavior-Based Robotics
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
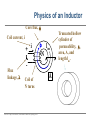
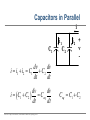
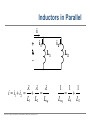
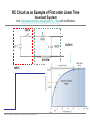
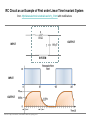
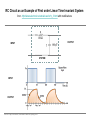
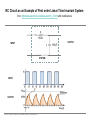
EE 1106: Introduction to EE Freshman Practicum Lecture-Lab: Introduction to signals and systems, RLC dynamical circuit Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Signals and Systems – Signal: • Any time dependent physical quantity • Constant – DC, Variable - AC • Electrical, Optical, Mechanical – System: • Object in which input signals interact to produce output signals. • Linear System has some have fundamental properties that make it predictable: – Sinusoid in, sinusoid out of same frequency (when transients settle) – Double the amplitude in, double the amplitude out (when initial state conditions are zero) Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 u(t) ? x(t) y(t) System Modeling • Building mathematical models based on observed data, or other insight for the system. – Parametric models (analytical): ODE, PDE – Non-parametric models: graphical models plots, look-up cause-effect tables – Mental models – Driving a car and using the cause-effect knowledge – Simulation models – Many interconnect subroutines, objects in video game Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Types of Models • White Box – derived from first principles laws: physical, chemical, biological, economical, etc. – Examples: RLC circuits, MSD mechanical models (electromechanical system models). • Black Box – model is entirely derived from measured data – Example: regression (data fit) • Gray Box – combination of the two Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 White Box Systems: Electrical • Defined by Electro-Magnetic Laws of Physics: Ohm’s Law, Kirchoff’s Laws, Maxwell’s Equations • Example: Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor i i i u Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 L C R u u Physics of an Inductor Core flux, f Coil current, i i + l Flux linkage, l Coil of N turns Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 f l m N A Truncated hollow cylinder of permeability, m, area, A, and length lm. Voltage Drop Across Inductor i L + v + l - Note Passive Sign Convention d l d m N 2 Ai m N 2 A di v dt dt lm lm dt m N2A di L vL lm dt Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Energy in an Inductor i L + v + l - di p vi Li dt p dt dw Li di Stored Energy 1 2 W Li di Li 2 Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Physics of a Capacitor Plate area, A Plate separation distance, g g i, q A e Current, i, and Charge, q. + v - Dielectric material of permittivity, e. Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Voltage across plates Physics of a Capacitor dq d e Av e A dv Current: i dt dt g g dt eA C Capacitance: g i, q Note Passive Sign Convention: C Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 + v - dv iC dt Energy in a Capacitor i C dv p vi Cv dt Stored Energy: + v - p dt dw Cv dv 1 2 W Cv dv Cv 2 Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Inductors in Series i L1 L2 + v1 - + v2 + v - di di v v1 v2 L1 L2 dt dt di di v L1 L2 Leq dt dt Leq L1 L2 Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Capacitors in Parallel i C1 i1 C2 i2 + v - dv dv i i1 i2 C1 C2 dt dt dv dv i C1 C2 Ceq dt dt Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Ceq C1 C2 Inductors in Parallel i i1 + l - i i1 i2 l L1 i2 L1 l L2 Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 l Leq L2 1 1 1 Leq L1 L2 Capacitors in Series q C1 q C2 q + v2 + v1 + v - q q q v v1 v2 C1 C2 Ceq 1 1 1 Ceq C1 C2 Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 RLC Circuit as a System R u u 1 u u 2 C u(t) RLC q(t) 3 L Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 i(t) RC Circuit as an Example of First order Linear Time Invariant System from http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/rc/rc_1.html with modifications OUTPUT SYSTEM INPUT Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 RC Circuit as an Example of First order Linear Time Invariant System from http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/rc/rc_3.html with modifications OUTPUT INPUT SYSTEM INPUT OUTPUT Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 RC Circuit as an Example of First order Linear Time Invariant System from http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/rc/rc_3.html with modifications OUTPUT INPUT SYSTEM INPUT OUTPUT Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 RC Circuit as an Example of First order Linear Time Invariant System from http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/rc/rc_3.html with modifications OUTPUT INPUT SYSTEM INPUT OUTPUT Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Integrator and Low Pass Filter from http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/rc/rc_3.html Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Differentiator and High Pass Filter from http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/rc/rc_3.html Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Lab 9 Circuits Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 Next Time: MSP 430, Bring Computer and Install Code Composer Dan O. Popa, Intro to EE, Freshman Practicum, Spring 2015 24