* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series Circuits
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
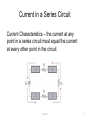
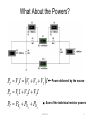
Series Circuits Series Circuit – a circuit that contains only one current path Circuit Diagram Constructed Circuit EGR 101 1 Total Series Resistance From our Breadboarding Experiment, we found that the total resistance of this circuit is 11.3 kΩ, which happens to be equal to the sum of all of the resistances in the series loop. RT R1 R2 ... Rn RT = the total circuit resistance Rn = the highest-numbered resistor in the circuit EGR 101 2 Current in a Series Circuit Current Characteristics – the current at any point in a series circuit must equal the current at every other point in the circuit EGR 101 3 Voltage Characteristics of a Series Circuit The voltages across the resistors “around the loop” add up to the applied Power Supply voltage. VS V1 V2 ... Vn EGR 101 4 What About the Powers? P PT Vs I V1 V2 V3 I Power delivered by the source PT V1 I V2 I V3 I PT PR1 PR2 PR3 Sum of the individual resistor powers EGR 101 5 EGR 101 6