* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glossary
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
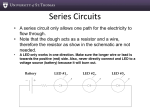
Intermediate 1 Physics Practical Electricity Glossary ammeter to circuit circuit breaker to consumer unit continuity to earth wire extension block to lamp live wire to neutral wire ohmmeter to power power station to series connection variable resistor to voltmeter Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 1 ammeter to circuit ammeter an instrument for measuring current it is connected in series ampere the unit for electric current appliance a device which is plugged into the mains e.g. television, washing machine etc. broken circuit a circuit with a gap in it no current can flow circuit a path round which electricity can flow Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 2 circuit breaker to consumer unit circuit breaker an automatic switch which breaks a circuit when a fault develops circuit symbol a simple picture to represent a component in a diagram complete circuit a circuit with no gaps in it electricity can flow component a part used in an electric circuit, e.g. lamp, resistor, fuse etc. consumer unit the board where the electricity supply comes into a house and goes through the meter and fuses Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 3 continuity to earth wire continuity this means whether a circuit has a break in it or not continuity tester a circuit for testing whether a circuit has a break in it current the flow of electricity round a circuit double insulated this means that an appliance has no outer parts which can become “live”. It does not need an earth wire in its flex. a safety connection. This helps to prevent a person from getting an electric shock if a fault occurs in an appliance. earth wire Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 4 extension block to lamp extension block a block of sockets which allows more appliances to be connected to the mains at one time function the “job” something does fuse a safety component. It melts and breaks the circuit if too high a current flows. this changes electrical energy to heat energy. It can be made from a piece of resistance wire. a component which changes electrical energy to light energy because it contains a wire (the filament) which heats up heater lamp Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 5 live wire to neutral wire live wire the brown wire in a plug which is at a high voltage mains electricity electricity supplied at 230 volts to homes in Britain motor a component which changes electrical energy to kinetic energy (it rotates) multimeter a meter which can be set to be used as an ammeter or as a voltmeter or as a resistance meter (ohmmeter) neutral wire the blue wire in a plug Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 6 ohmmeter to power ohmmeter a meter used to measure the resistance of a component ohms the units of resistance open circuit an electrical path which has a break in it parallel connection this type of connection has a split in the wiring to allow a choice of paths for the current power the amount of energy per second, measured in watts. 1 kW = 1 kilowatt = 1000 W Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 7 power station to series connection power station a place where mains electricity is generated (often by burning coal) power supply a device (like a labpack) which gives out a variable voltage resistance the opposition to current it is measured in ohms (W) resistor a component which restricts the current in a circuit series connection components connected so that the current has only one path though the circuit Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 8 variable resistor to voltmeter variable resistor a resistor whose value can be changed voltage the electrical “push” of a supply, e.g. a 9.0 V battery provides more energy than a 3.0 V one voltmeter this device measures the voltage across any supply or component Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 9 Intermediate 1 Physics Practical Electricity Glossary End of Glossary Beath High School - Int 1 Physics 10