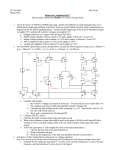
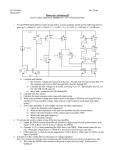
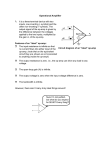
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an Op-Amp? - benchmark
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Operational Amplifiers Benchmark Companies Inc PO Box 473768 Aurora CO 80047 What is an Op-Amp? INTRODUCTION What is an operational amplifier? In this chapter, we will define what an operational amplifier is, and discuss the many parameters that distinguish one type of device from another. What is an Op-Amp? OBJECTIVES At the completion of this chapter, you will be able to define the following: • Define the following terms: channel separation closed-loop gain common-mode rejection ratio gain-bandwidth product input bias Current offset input offset Current input offset voltage Input resistance input voltage range inverting input loop gain non-inverting input open-loop gain operational amplifier output resistance output voltage swing slew rate What is an Op-Amp? Objective cont. Interpret a typical op-amp data sheet. Measure some of the common op-amp parameters. What is an Op-Amp? THE IDEAL OP-AMP Before we start looking at actual operational amplifier circuits, we will briefly consider the operational amplifier, hereafter referred to Op amp, by itself. What is an Op-Amp? THE IDEAL OP-AMP The term Op-amp was originally used to describe a series of high-performance dc amplifiers that were used as the basis for analog computers. What is an Op-Amp? THE IDEAL OP-AMP Today’s integrated circuit op-amp is a very high-gain dc amplifier that uses external feedback networks to control its response. Feedback What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop Mode The op-amp without any external feedback is described as being used in an open-loop mode. What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop Mode It is in this mode that we can describe the characteristics of the ideal op-amp: The open-loop gain is infinite. What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop Mode It is in this mode that we can describe the characteristics of the ideal op-amp: The input resistance is infinite. The output resistance is zero. What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop Mode It is in this mode that we can describe the characteristics of the ideal op-amp: The bandwidth is infinite. The output voltage is zero when the input voltage is zero (i.e., zero offset). What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop Mode In practice, however, no op-amp can meet these five ideal open-loop characteristics. However, as we shall see in the next few chapters, the world doesn’t come to an end because there is no such thing as the ideal op-amp. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP SCHEMATIC SYMBOL the op-amp has two inputs: one inverting, or input, and one non-inverting, or + input. a single output Inverting Output Non-Inverting What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP SCHEMATIC SYMBOL the op-amp is powered normally by a dual-polarity power supply, typically in the range of ±5 to ± 15 volts. Neg Pos What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Perhaps the best way to understand the many characteristics of an op-amp is to examine a manufacturer’s data sheet. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET the data sheet usually contains the following information: A general description of the op-amp. An internal equivalent circuit schematic. Pin configuration of the device. The absolute maximum ratings. The electrical characteristics. Typical performance curves. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET we will cover most of the important parameters, using the type 741 op-amp as a representative example. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Important Parameters cont. Maximum Ratings: The maximum ratings given in the data sheet are the maximum the op-amp can safely tolerate without the possibility of destruction. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Maximum Ratings: Supply Voltage (±Va ) This is the maximum positive and negative voltage that can be used to power the op-amp. Internal Power Dissipation (PD) This is the maximum power that the op-amp is capable of dissipating, given a specified ambient temperature (i.e., 500 mW @ <75C). Differential Input Voltage (Vid ) This is the maximum voltage that can be applied across the + and - inputs. Input Voltage (Vicm ) This is the maximum input voltage that can be simultaneously applied between both inputs and ground, also referred to as the common-mode voltage. In general, this maximum voltage is equal to the supply voltage. Operating Temperature (Ta) This is the ambient temperature range for which the op-amp will operate within the manufacturer’s specifications. Note that the military grade version (741) has a wider temperature range than the commercial, or hobbyist, grade version (741C). Output Short-Circuit Duration This is the amount of time that the op-amp’s output can be short-circuited to ground or either supply voltage. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Important Parameters cont. Electrical Characteristics: The Op amp’s electrical characteristics are usually specified for a supply voltage and ambient temperature. However, certain parameters may also have other conditions attached, such as a particular source resistance. Generally, each parameter will have a minimum typical, and/or maximum value. (See data sheet for examples) What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Electrical Characteristics: cont. Input Parameters: Input Offset Voltage (Voi) This is the voltage that must be applied to one of the input terminals to give a zero output voltage. Remember, for an ideal op-amp, the output voltage offset is zero! Input Bias Current (Ib) This is the average of the currents flowing into both inputs. Ideally, the two input bias currents are equal. Input Offset Current (los) This is the difference of the two input bias currents when the output voltage is zero. Input Voltage Range (Vcm ) This is the range of the common-mode input voltage (i.e., the voltage common to both inputs and ground). Input Resistance (Zi) This is the resistance “looking in” at either input with the remaining input with the remaining input grounded. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Electrical Characteristics: cont. Output Parameters: Output Resistance (Zoi) This is the resistance seen “looking into” the op-amp’s output. Output Short-Circuit Current (Iosc ) This is the maximum output current that the op-amp can deliver to a load. Output Voltage Swing (±Vo max) Depending on the load resistance, this is the maximum peak output voltage that the op-amp can supply without saturation or clipping. What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Electrical Characteristics: cont. Dynamic Parameters: Open-Loop Voltage Gain (AOL) This is the ratio of the output to input voltage of the op-amp without external feedback. Large-Signal Voltage Gain This is the ratio of the maximum voltage swing to the change in the input voltage required to drive the output from zero to a specified voltage (e.g., ±10 volts). Slew Rate (SR) This is the time rate of change of the output voltage with the opamp circuit having a voltage gain of unity (1.0). What is an Op-Amp? THE OP-AMP DATA SHEET Electrical Characteristics: cont. Other Parameters: Supply Current This is the current that the op-amp will draw from the power supply Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) This is a measure of the ability of the op-amp to reject signals that are simultaneously present at both inputs. It is the ratio of the common-mode input voltage to the generated output voltage, usually expressed in decibels (dB). Channel Separation Whenever there is more than one op-amp in a single package, such as a type 747 op-amp, a certain amount of “crosstalk” will be present. That is, a signal applied to the input of one section of a dual op-amp will produce a finite output signal in the remaining section, even though there is no input signal applied to the unused section. What is an Op-Amp? GAIN AND FREQUENCY RESPONSE Unlike the ideal op-amp, the Op-amp that is used in various circuits does not have infinite gain and bandwidth. As shown in Fig.1, the open-loop gain AOL for a type 741 op-amp is graphed as a function of frequency. What is an Op-Amp? GAIN AND FREQUENCY RESPONSE At very low frequencies, the open-loop gain of opamp is constant, but begins to “roll off” at approximately 6 Hz at a rate of -6 dB/octave or -20 dB/decade An octave is a doubling in frequency and a decade is a ten-fold increase in frequency. What is an Op-Amp? GAIN AND FREQUENCY RESPONSE This decrease continues until the gain is unity, or 0 dB. The frequency at which the gain is unity is called the unity gain frequency, fT. What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop and Closed Loop Gain When some of the output signal is fed back to the op-amp’s input, the ratio of the output to input voltage is termed the closed-loop gain, ACL, and is always less than the open-loop gain. What is an Op-Amp? Open Loop and Closed Loop Gain The difference in decibels between the open-loop and closed-loop gains is the loop gain, AL. When AOL and ACL are expressed as simple output-to-input ratios, the loop gain is expressed mathematically as: AL = AOL/ACL What is an Op-Amp? Gain Bandwidth Perhaps the first factor in the consideration of a particular op-amp for a given application is its gain-bandwidth product, or GBP. What is an Op-Amp? Gain Bandwidth For the response curve below, the product of the open-loop gain and frequency is a constant at any point on the curve, so that: GBP =AOLBW What is an Op-Amp? Gain Bandwidth Graphically, the bandwidth is the point at which the closed-loop gain curve intersects the open-loop gain curve, as shown in the figure below for a family of closed-loop gains. What is an Op-Amp? Gain Bandwidth Therefore, one obtains the bandwidth for any desired closed-loop gain by simply drawing a horizontal line from the desired value of gain to intersect the roll-off of the open-loop gain curve. What is an Op-Amp? Gain Bandwidth For a practical design situation, the actual design gain of an opamp circuit should be about a factor of 1/10 to 1/20 of the open-loop gain at a given frequency. What is an Op-Amp? Gain Bandwidth This ensures that the op-amp will function properly without distortion. As an example, using the response of Fig. 1-3, the closed-loop gain at 10 kHz should be about 5 to 10, since the open-loop gain is 100 (40 dB). ACL What is an Op-Amp? Transient Response, (Rise Time) The time that it takes for the output signal to go from 10% to 90% of its final value when a step. Input Signal Output Signal time Timing Diagram What is an Op-Amp? Transient Response, (Rise Time) A function pulse is used as an input signal, and is specified under closed-loop conditions. From electronic circuit theory, the rise time is related to the bandwidth of the op-amp by the relation: BW= 0.35/rise time What is an Op-Amp? Summary Op-amps are designed to be powered from a dual, or bipolar, voltage supply which is typically in the range of ±5 to ±15 volts. What is an Op-Amp? Summary That is, one supply is +5 to +15 volts with respect to ground, and another supply voltage of -5 to -15 volts with respect to ground. What is an Op-Amp? Summary However, in certain cases, an op-amp may be operated from a single supply voltage, which is explained in Chapters 8 and 9. End of Lesson