* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digital Signal Processing
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
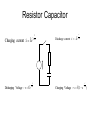
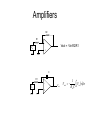
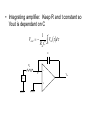
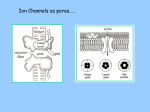
Input technologies • All require some form of data acquisition – e.g. Image scanner, Microphone • Once acquired, if the signal is not already digital, it will need to be converted using a A to D converter. • Image scanners for scanning fingerprints for example, tend to use one of two scanning technologies: optical and capacitive. – What is capacitive? General recognition block diagram Input Electronics Image capture Sound capture Pen capture A to D Pre-proc Reco Output Electronics Monitor Brail pins Printer Speaker Intro to common components • Hardware is used at the extreme input and output so a basic understanding is necessary • Resistor (Ohms) – Current directly proportional to Voltage – Current inversely proportional to resistance • Capacitor (Farads) – Charge storage – Current is proportional to capacitance and rate of change of voltage – Capacitance is directly proportional to plate area and inversely proportional to plate distance Common components • Voltage amplifier – Typically inverts so Vout = -A.Vin • Charging a capacitor via a resistor – Capacitor charges non-linearly – http://www.lon-capa.org/~mmp/kap23/RC/app.htm Resistor Capacitor Charging current : i Iˆe Disharging Voltage : v Vˆe t CR t CR Discharge current : i Iˆe t CR Charging Voltage : v Vˆ (1 e t CR ) Amplifiers R2 R1 - Vout = -Vin.R2/R1 Vin + C R1 Vin + Vout Vout 1 t Vin d 0 Rin C Capacitive scanning • Skin has electrical properties such as resistance and capacitance so can be used to control electric current • A touch switch for example relies on either the resistance of the skin to bridge two contacts to pass an electric current or to bridge two contacts to connect a capacitance in a circuit. • An array of electrical contacts placed at a resolution of less than the width of a finger print ridge • The nearer the skin is to the contact, the higher the capacitance value – so a ridge would create a high capacitance value at each set of contacts it touches • Each set of contacts connects the feedback loop of an integrating amplifier C R i V i n n P + V ou t • Integrating amplifier. Keep R and t constant so Vout is dependant on C Vout 1 t . Vin d 0 Rin C C Rin P Vout Vin + Microphone • 3 main types – Dynamic • Electromagnetic using moving coil – Condenser • Electrostatic. Needs a voltage source – Electret • Similar to condenser but does not need voltage source Dynamic microphone • Like a loudspeaker in reverse Condenser microphone Area Capacitance Distance •Sound cards provide voltage through connector Electret microphone • The electret condenser mic uses a special type of capacitor which has a permanent voltage built in during manufacture. This is can be likened to a permanent magnet, in that it doesn't require any external power for operation. Otherwise it operates in the same way as a condenser microphone Capacitance scanner operation • Finger is placed on the scanner • All capacitances are short circuited to discharge any residual charge in the contacts • The resistance is constant and a DC voltage is applied to the input for a fixed time • The voltages at the outputs of the integrators is input to an A to D converter Loudspeaker Optical Scanning • Generally use a Charge Coupled Device (CCD). – Array of photodiodes which generate an electric current in response to being struck by light photons – i.e. output is analogue. – An A to D converter converts the analogue variation from each cell into a binary number representing brightness Image Sensor Operation • Charge Coupled Device image sensor • Background is image sensor zoomed in • CCD measures brightness • Tiny lenses direct light onto filtered photosensitive regions • More green than red to better match the eye Bayer filter • Eye responds mostly to green so as many green filters as red+blue • Demosaic – interpolate a single pixel colour by interpolating nearest neighbours as each pixel only records one colour so the actual colour at that point is the average of it and the surrounding pixels CCD Operation CCD Operation • Charge is moved down 1 row at a time then clocked out to an amp and A to D converter • CCD device used to photograph the finger when placed on the glass • Light source is usually an array of LEDs to enable sharp capture of fingerprint ridges – Image processing techniques (covered later in the module) check the contrast and sharpness of the captured image and adjusts the light source (or generates instructions to the user) if necessary Pros, Cons and Limitations • Capacitance scanner can not be shown a picture of a fingerprint for recognition so is not as easily fooled as CCD • Capacitance scanners tend to be smaller • Both can be fooled by latex copy or by chopping off someone's finger • Some systems have heat / pulse sensors – Can put latex copy over real finger to fool these • Better to use additional biometrics / password Fingerprint Recognition • Comparing one whole fingerprint to another by direct comparison is infeasible as the contrast may be different, pressure and orientation may be slightly different … • Most recognition technologies look for specific features whether this is fingerprint or speech recognition as a lot of the data defining uniqueness is redundant Fingerprint characteristics • The scanned image shows ridges as black and valley’s as white areas • Characteristics are called minutiae (mi-NOO-shee-ee ) – Ridge ends (A) – Bifurcations (B) ridge splits from 1 to 2 • Image needs to be pre-processed to enhance it • Algorithms needed to used to identify minutiae General recognition block diagram Input Electronics Image capture Sound capture Pen capture A to D Pre-proc Reco Output Electronics Monitor Brail pins Printer Speaker Summary • As will be seen with most recognition technologies: – data is captured – analogue to digital conversion – enhanced (e.g. contrast enhance) – Feature extraction (in this case minutiae) – Recognition algorithm