* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint-presentation
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Hendrik Wade Bode wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
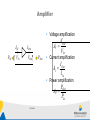
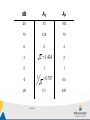
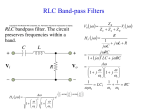
2017-05-23 Analog Electronics http://www.miun.se/personal/kent.bertilsson/Courses/AnalogElectronics.htm • Thomas L. Floyd, "Electronic Devices - Conventional Current Version" ISBN: 0-13-615581-2 • Don Manchini, "Op Amps for Everyone" -Free downloadable pdf Lecturer Lab teacher Kent Bertilsson Krister Hammarling [email protected] S-Building Office S206 Phone 060-148915 [email protected] S-Building Office S207 2017-05-23 Examination This analog electronics is given as a stand alone course but also as one part of the Measurement System course. • 12 x 2h scheduled lectures – 10 Lectures – 2 times for solving problems • As appeared in the plan (Not as shown in schedule) • 4 x 4h scheduled laboratory classes completing 3 tasks that should completed and handed in to the laboratory teacher. • A written exam will be held 27th October 2017-05-23 Introduction 2017-05-23 Block Diagram • Electronic systems is often described by block diagram Antenna Amplifier 2017-05-23 Filter Analog to digital conversion Time domain vs Frequency domain • Every signal can be described both in the time domain and the frequency domain. • A periodic signal (in the time domain) can in the frequency domain be represented by: – A peak at the fundamental frequency for the signal, fs=1/T – and multiples of the fundamental f1,f2,f3,…=1xfs ,2xfs ,2xfs V V T=1/fs t fs 2017-05-23 2 fs 3 fs 4 fs 5 fs f Time domain vs Frequency domain • Every signal can be described both in the time domain and the frequency domain. • A non periodic (varying) signal time domain is spread in the frequency domain. • A completely random signal (white noise) have a uniform frequency spectra V V fs 2 fs 3 fs 4 fs 5 fs 2017-05-23 f Noise f Transfer function • The transfer function is the relation between the amplitude for the output and input in the frequency domain. U Out f Hf U in f – H(20kHz)=10 mean that for a 20kHz signal the output is ten times larger than the input. – H(f) is of course continuous function H 10 5 0 f 2017-05-23 Filter • A filter is a circuit that let some frequencies pass and H block others. – Low pass f H – High pass f H – Band pass f H – Band stop f 2017-05-23 jω-method • The jω-method is a very powerful tool making it possible performing advanced frequency dependent (alternating current, AC) functions using the same rules that applies for direct current (DC) Resistor Capacitor Inductor X R 1 X jC X jL Symbol Reactance 2017-05-23 jω-method • Impedance calculations can be performed in the same way as for normal resistances. R L R L Z Z R Z L R jL 1 R Z R ZC R j C Z Z R // Z C Z R ZC R 1 1 jRC jC 2017-05-23 RC - filter Calculate the transfer function H(ω) R VIn C What is the output voltage and power level at the cut-off frequency? VOut 2017-05-23 Amplifier • Voltage amplification PIN IIN IOut VIn VOut POut VOut AV VIn • Current amplification I Out AI I In • Power amplification POut AP PIn 2017-05-23 Decibel, dB decibel, dB is very useful expressing amplification (and attenuation) APdB APdB POut 10 log AP 10 log PIn V2 P V I (Under assumption R that RInAmp=RLoad) 2 VOut 2 VOut POut VOut R 10 log 10 log 2 10 log 20 log VIn PIn VIn VIn R VOut AVdB 20 log AV 20 log VIn 2017-05-23 dB AV AP 20 10 100 10 3.16 10 6 2 4 2 1.414 3 0 1 1 -3 2 -20 2017-05-23 2 1 0.707 0.5 0.1 0.01 Bode Diagram • Absolute decibel value and phase of the transfer function is plotted against a logarithmic frequency axis H f dB angle H f 2017-05-23 RC-filter example Draw an asymptotic bode diagram for the RC filter. R VIn C VOut 2017-05-23 Bode diagram • Complicated expressions can be factorized into sub-expressions as Const Differentiator Zero C j 1 j 0 2017-05-23 1 j 1 1 j 0 Integrator Pole Bode diagram • According to logarithmic laws Atot A1 A2 A3 Atot dB A1dB A2 dB A3 dB angle Atot angle A1 angle A2 angle A3 2017-05-23 Example R VIn R2 Draw an asymptotic bode diagram for the shown filter. C R3 VOut 2017-05-23 Amplifier model • The amplifier model is often sufficient describing how an amplifier interacts with the environment ROut VIn RIn AVVIn VOut • RIn – Input impedance • AV – Voltage gain • ROut – Output impedance 2017-05-23 Bandwidth • The bandwidth is the frequency range where the transferred power are more than 50%. AP 0.5 AP max H(f) AVmax 0.707AVmax AV 2 AV max 0.707 AV max B f 2 f1 f1 2017-05-23 f2 f Distortion • A nonlinear function between UIn and UOut distorts the signal – An amplifier that saturates at high voltages – A diode that conducts only in the forward direction 2017-05-23 Noise • Random fluctuation in the signal • Theoretically random noise contains all possible frequencies from DC to infinity • Practical noise is often frequency limited to an upper bandwidth by some filter • A limited bandwidth from the noisy reduce the noise power 2017-05-23