* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digital to Analog Converters (DAC)
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
MOS Technology SID wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
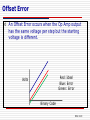
Digital to Analog Converters (DAC) 2 Technician Series ©Paul Godin Created March 2015 R/2R DAC ◊ The Binary-Weighted DAC limitations include the need for progressively larger resistors. ◊ The R/2R ladder method eliminates the need for the variety of resistors required. It operates on a ratio between resistors. ◊ The Op Amp is still an important component in the circuit. DAC 2.2 R/2R Circuit LSB MSB Rf 2R 2R 2R 2R R R 2R VDD R VEE The resistance seen to the right of any vertical resistor is 2R. DAC 2.3 Other Types of DACs ◊ MOSFET Current Scaling that use a configuration of MOSFETs in a similar manner to R/2R. ◊ Voltage Scaled DACs employ a resistor string as a large voltage divider for reference voltage values, and use enable/disable circuitry for the output voltage. ◊ Charge Scaling DACs utilize capacitors instead of resistors. Can be more accurate and potentially faster but are more difficult to implement. DAC 2.4 Typical DAC chip (DAC 08) B1-B8: Binary inputs Io & Io’: Analog Output V- & V+: Supply Voltages VLC & Comp: Special Purpose Most DACs are designed to output current, not voltage. An external resistor is needed to convert current to voltage. The value of this resistor can aid in scaling the output. DAC 2.5 ERRORS IN DAC DAC 2.6 Errors ◊ Digital to Analog systems have several possible sources of error. ◊ The errors can be the result of: ◊ Binary Input ◊ Non-linear input sequences or incorrect values ◊ Voltage issues ◊ Resistor network ◊ Resistors out of specification ◊ Noise ◊ Op Amp output errors ◊ Improper input voltage ◊ Improper Offset ◊ Delay DAC 2.7 Gain Error ◊ A Gain Error occurs when the Op Amp produces an output at a different voltage scale than desired. The output is linear but the steps are either larger or smaller than they should be. Output may appear clipped. Red: Ideal Blue: Error Green: Error Volts Binary Code DAC 2.8 Gain Error Typical Causes: •wrong VDD/VEE at op amp •wrong RREF value •wrong resistor network values Red: Ideal Blue: Error Green: Error DAC 2.9 Offset Error ◊ An Offset Error occurs when the Op Amp output has the same voltage per step but the starting voltage is different. Red: Ideal Blue: Error Green: Error Volts Binary Code DAC 2.10 Offset Error Typical Causes: •op amp improperly offset Red: Ideal Blue: Error Green: Error DAC 2.11 Non-Linearity: Non-Monotonic ◊ A Monotonic Error occurs when the individual voltage steps are non-linear. Red: Ideal Blue: Error Volts Binary Code DAC 2.12 Non-Linearity: Non-Monotonic Typical Causes: •incorrect input binary sequence caused by mix-up at binary input or a stuck input Red: Ideal Blue: Error DAC 2.13 Non-Linearity: Differential ◊ A Differential Error occurs when the output steps start to vary in size. Red: Ideal Blue: Error Volts Binary Code DAC 2.14 Non-Linearity: Differential Typical Causes: •resistor network unbalanced •binary input voltage values Red: Ideal Blue: Error DAC 2.15 END DAC 2 ©Paul R. Godin prgodin°@ gmail.com DAC 2.16