* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DAC_WangChen
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
MOS Technology SID wikipedia , lookup
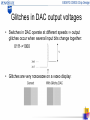
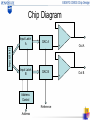
EE597G Presentation: Design of Digital-to-Analog Converter Qin Chen Yong Wang Dept. of Electrical Engineering Feb. 6th, 2006 What’s DAC? Smpl Object A/D Digital System D/A Ctrl Object • A device that converts digital signals to analog signals • It’s usually used to control analog devices, such as actuator, audio and video output. Weighted-Resistor DAC – VOUT is a weighted sum of V3, …, V0 with weights proportional to the conductances G3, .., G0. – If X3:0 is a binary number we want conductances in the ratio 8:4:2:1. –Fast: gate slew rate ≈ 3 V/ns. – We can scale the resistors to give the output impedance we want. – Not good for many bits DAC R-2R Ladder • resistances of the two branches at V1 both equal 2R so the current into this node will split evenly. • using only two resistor values, can generate a whole series of currents where In=2nI0. • From the voltage drop across the • horizontal resistors, we see that • Vn = 2RIn = 2n+1RI0 . For an Nbit ladder the input voltage is therefore I0=2–N Vin/R. Current-Switched DAC • Total current into summing junction is X3:0 ×I0, Vout = X3:0 × Vin /16R × (–Rf) • Use CMOS transmission gates as switches: adjust ladder resistors to account for switch resistance. • All the switch output terminals are at 0 V. Ladder outputs are always connected either to ground or to a virtual earth. Advantages: • Very fast, No need to charge/discharge node capacitances • Only two value resistors can satisfy many bits DAC Glitches in DAC output voltages • Switches in DAC operate at different speeds ⇒ output glitches occur when several input bits change together: 0111->1000 • Glitches are very noticeable on a video display: Deglitching with sample/hold circuit • To minimize the effect of glitches: – Use a register to make inputs change as simultaneously as possible – Use a sample/hold circuit to disconnect the DAC output while it is changing Chip Specifications • • • • • • Resolution: 8 bits No. of channels: 2 Interface: Parallel Output type: Voltage Reference: External Supply voltage: Single, 5V Chip Specifications (cont.) • • • • • • Power consumption (Max. 200mW) Update rate (100MHz) Settling time (10μs) Area (1mm2) Integral Nonlinearity ( 1 LSB) Differential Nonlinearity (1 LSB) Chip Diagram - DAC A + Input(8 bit) Input Latch A Out A Input Latch B DAC B + Address Control Reference Address Out B Project Schedule Week 1 Systematic design of chip Week 2 Systematic design of chip (cont.) Week 3 Circuit design Week 4 Circuit design (cont.) Week 5 Layout design Week 6 Layout design (cont.) Week 7 Final adjustments and verification Week 8 Final adjustments and verification (cont.)