* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced Analog Circuits
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
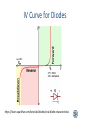
Advanced Analog Circuits Seth Price Department of Chemical Engineering New Mexico Tech Rev. 1/26/15 Diodes (PN Junction) • • • • Diodes conduct in only one direction Semiconducting device Resistance is non-linear Require a “knee” or “turn-on” voltage – Silicon: 0.6-0.7V – Germanium: 0.3V – LED: 1.7V Diode Vs. Sine Wave • http://www.duncansonelectric.com/blog/wpcontent/uploads/2009/08/23-half-wave-rectifier-1024x368.gif IV Curve for Diodes https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/diodes/real-diode-characteristics Zener Diode • Diode that is meant to operate in reverse bias region – Very stable, consistent voltage • Can be used to replace battery, complex resistor network in some situations Capacitors • Store energy in an electric field • Measured in Farads (F) • Two physical configurations – Parallel plates – Concentric cylinders Capacitor Combinations • Series Combination: • 1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + … + 1/Cn • Parallel Combination: • Ceq = C1 + C2 + … + Cn Capacitor Voltage Vc(t) = Vs(1-e-t/T) • Vc(t): Voltage across capacitor at any time • Vs: Source voltage • T: Time constant • t: elapsed time Inductors • Store energy in a magnetic field • Measured in Henries (H) • Typically a coil of wire • Adjustable inductor: slug Inductor Combinations • Series Combinations • Leq = L1 + L2 + … + Ln • Parallel Combinations • 1/Leq = 1/L1 + 1/L2 + … + 1/Ln Inductor Voltage V(t) = -L * di/dt • V(t): Voltage across Inductor as a function of time • L: inductance in Henries • di/dt: change in current with respect to time Time Constants • Time Constant (T): way to characterize time to charge/discharge a capacitor or inductor • 1*T: 63% of the maximum charge • 5*T: fully charged • For a capacitor: T = R*C • For an inductor: T = L/R Solenoids • Changing current induces magnetic field • Magnetic field moves plunger • Used in starter motors, valves, latches, etc. Solenoid Valve Transformers • Two adjacent inductors that can influence each other • Can add an iron core to transformer to increase magnetic field • No electron travels between inductors – Isolation Transformer Transistors • Semiconducting device • Used as switches, amplifiers, attenuators, impedance matching, etc. • Two major categories (NPN, PNP) • Types: BJT, MOSFET, JFET, etc. Putting it all together… • DC Power Supply