* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Operating System Overview
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT startup process wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Thread (computing) wikipedia , lookup
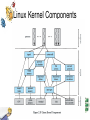
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Patricia Roy Manatee Community College, Venice, FL ©2008, Prentice Hall Windows Architecture • Modular structure for flexibility • Executes on a variety of hardware platforms • Supports applications written for other operating system Kernel-Mode Components • Executive – Contains base operating system services • • • • • Memory management Process and thread management Security I/O Interprocess communication Kernel-Mode Components • Kernel – Consists of the most used components • Hardware abstraction layer (HAL) – Isolates the operating system from platformspecific hardware differences Kernel-Mode Components • Device drivers – Translate user I/O function calls into specific hardware device I/O requests • Windowing and graphics systems – Implements the graphical user interface (GUI) Windows Executive • • • • • I/O manager Cache manager Object manager Plug and play manager Power manager Windows Executive • • • • • Security reference monitor Virtual memory manager Process/thread manager Configuration manager Local procedure call (LPC) facility User-Mode Processes • Special system processes – Ex: session manager, authentication subsystem, service manager logon process • Service processes • Environment subsystems • User applications Client/Server Model • Simplifies the Executive – Possible to construct a variety of APIs • Improves reliability – Each server runs outside the kernel, protected from other servers Client/Server Model • Provides a uniform means for applications to communicate via RPCs • Provides base for distributed computing Threads and SMP • Operating system routines can run on any available processor • Multiple threads of execution within a single process may execute on different processors simultaneously Threads and SMP • Server processes may use multiple threads • Share data and resources between process Windows Objects • Encapsulation – Object consists of one or more data items and one or more procedures • Object class and instance – Create specified instances of an object Windows Objects • Inheritance – Supported to some extent in the Executive • Polymorphism UNIX • Hardware is surrounded by the operating system software • Comes with a number of user services and interfaces – Shell – Components of the C compiler General UNIX Architecture Traditional UNIX Kernel Modern UNIX Kernel Modern UNIX Systems • System V Release 4 (SVR4) • BSD • Solaris 10 Linux • Does not use a microkernel approach • Collection of loadable modules – Dynamic linking – Stackable modules Linux Kernel Modules Linux Kernel Components