* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lect03
Linux adoption wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
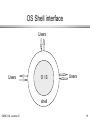
Operating Systems I An Introduction to Operating System Concepts CMSC 104, Lecture 03 1 What is an Operating System (OS)? • A computer program • Performs many operations, such as: • Allows you to communicate with the computer (tell it what to do) • Controls access (login) to the computer • Keeps track of all processes currently running CMSC 104, Lecture 03 2 How Do I Communicate With the Computer Using the OS? • You communicate using the particular OS’s user interface. • Graphical User Interface (GUI) - Windows • Command-driven interface - DOS, UNIX, Linux • We will be using the Linux operating system, which is very similar to UNIX. CMSC 104, Lecture 03 3 How Do I Communicate With the Computer Using the OS? (con’t) • When you log in to the Linux system here, a user prompt will be displayed: linux#[1]% _ where # is the number of the Linux server that you have connected to. You may use any of the Linux servers. • The number in the brackets will change as you work It is the “number” of the command that you are about to type. • If this prompt is not on the screen at any time, you are not communicating with the OS. CMSC 104, Lecture 03 4 OS Introduction • • • Computer applications today require a single machine to perform many operations and the applications may compete for the resources of the machine. This demands a high degree of coordination This coordination is handled by system software known as the operating system CMSC 104, Lecture 03 5 Evolution of Operating System • OS for batch jobs o Program execution required significant preparation of equipment o Program execution (job) o OS was a system to simplify program setup and simplify transition between jobs o Physical separation of users and equipment led to computer operators CMSC 104, Lecture 03 6 OS Evolution (cont’d) o Users left jobs with the operator and came back the next day (batch jobs) o Users had no interaction with computer during program execution. Maybe okay for some applications, but not for all. CMSC 104, Lecture 03 7 OS Evolution • OS for Interactive Processing o Allowed programs to carry on dialogue with user via remote terminals (workstations) o Real-time processing o Users demand timely response o Machines too expensive to serve only one user o Common for several users to want interactive services at the same time CMSC 104, Lecture 03 8 OS Evolution (cont’d) • OS for time-sharing o To accommodate multiple real-time users, the OS rotates its various jobs in and out of execution via time-sharing o Each job gets a predetermined “time slice” o At end of time slice current job is set aside and a new one starts o By rapidly shuffling jobs, illusion of several jobs executing simultaneously is created CMSC 104, Lecture 03 9 OS Evolution (cont’d) o Without time slicing, a computer spends most of its time waiting for peripheral devices or users o A collection of tasks can be completed in less time with time-sharing than when completed sequentially CMSC 104, Lecture 03 10 Different Operating Systems on the Same Machine ? • • • It is possible to have more than one operating system available to be used on a machine. Only one operating system is run at a time, though. Examples: o VAX -- VMS or Ultrix o PCs -- DOS, Windows, or Linux CMSC 104, Lecture 03 11 Types of software • Applications software o • Performs tasks specific to the machine’s utilization. System Software o o Performs tasks common to computer systems in general Operating systems vary based on the hardware they’re used on CMSC 104, Lecture 03 12 Types of software (cont’d) • Utility software o Provides fundamental activities, yet not included with OS o “Extends” the OS o Distinction between applications and utilities is often vague o Distinction between OS and utilities is also vague CMSC 104, Lecture 03 13 The OS Shell • Defines interface between OS and users o Windows GUI o UNIX command line o UNIX users can choose among a variety of shells •csh is the “C shell” •tcsh is an enhanced “C shell” CMSC 104, Lecture 03 14 OS Shell interface Users Users O/S Users shell CMSC 104, Lecture 03 15 The OS Kernel • • The internal part of the OS is often called the kernel Kernel Components o File Manager o Device Drivers o Memory Manager o Scheduler o Dispatcher CMSC 104, Lecture 03 16 OS File Manager • • • Maintains information about the files that are available on the system Where files are located in mass storage, their size and type and their protections, what part of mass storage is available Files usually allowed to be grouped in directories or folders. Allows hierarchical organization. CMSC 104, Lecture 03 17 OS Device Drivers • • • Software to communicate with peripheral devices or controllers Each driver is unique Translates general requests into specific steps for that device CMSC 104, Lecture 03 18 OS Memory Manager • • • Responsible for coordinating the use of the machine’s main memory Decides what area of memory is to be allocated for a program and its data Allocates and deallocates memory for different programs and always knows what areas are free CMSC 104, Lecture 03 19 OS Scheduler • Maintains a record of processes that are present, adds new processes, removes completed processes o memory area(s) assigned o priority o state of readiness to execute (ready/wait) CMSC 104, Lecture 03 20 OS Dispatcher • • • Ensures that processes that are ready to run are actually executed Time is divided into small (50 ms) segments called a time slice When the time slice is over, the dispatcher allows scheduler to update process state for each process, then selects the next process to run CMSC 104, Lecture 03 21 OS Summary • • • • • Shell -- interface to user File Manager -- manages mass memory Device Drivers -- communicate with peripherals Memory Manager -- manages main memory Scheduler & Dispatcher -- manage processes CMSC 104, Lecture 03 22 Utilities • • • • Operating systems usually come with some associated utility programs UNIX usually has the text editors xemacs/emacs and vi (and sometimes pico) UNIX has its own sort utility UNIX has its own mail utility CMSC 104, Lecture 03 23