* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
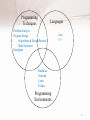
CS 161 INTRO TO PROGRAMMING I Dr. Blaise W. Liffick Fall 2014 1 Programming Techniques Languages Problem Analysis Program Design •Algorithms & Design Patterns •Data Structures Paradigms Java C++ Hardware Network Linux Eclipse Programming Environments 2 Early Computers • Late 1930’s, John Atanasoff, Clifford Berry • ENIAC – – – – 1946 University of Pennsylvania J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchley John von Neumann, stored-program concept and use of binary 3 Categories of Computers • • • • • Supercomputers Mainframe Minicomputers Microcomputers Mobile devices Power Size Cost 4 Computer Hardware • CPU - central processing unit – Where decisions are made, computations are performed, and input/output requests are delegated • Main Memory – Stores information being processed by the CPU • Secondary Memory (Mass Storage) – Stores data and programs 5 Computer Hardware • Input devices – Allow people to supply information to computers • Output devices – Allow people to receive information from computers • Peripheral Devices – Generally I/O, mass storage • Network connection – Modems – Ethernet interface 6 Figure 1.2 Computer components Mass storage 7 CPU • “Brains” of the computer – Arithmetic calculations are performed using the Arithmetic/Logical Unit or ALU – Control unit decodes and executes instructions – Registers hold information and instructions for CPU to process • Arithmetic operations are performed using binary number system 8 Memory • Stores – programs • operating system • applications – data • Types – RAM - volatile – ROM • Composed of bits, which are combined into bytes 9 Memory Cells Address Contents 0 1 2 3 -27.2 354 0.005 -26 4 5 6 H RTV 001 ... ... 999 X 75.62 10 Input / Output Devices • Accessories that allow computer to perform specific tasks – Receiving information for processing – Return the results of processing • Common input and output devices – Keyboard – Printer Joystick Monitor Scanner Speaker 11 Computer Networks • Allows multiple computers to connect together to share resources and/or data • LAN - Local area network – Organizational • WAN - Wide area network – Internet • Requires additional hardware – modem – network interface – servers 12 The “Cloud” • Wireless access – WiFi – Cell • Servers – Storage – Applications 13 World Wide Web • Introduced 1989 • Developed by CERN – European Laboratory for Particle Physics • Web browser - GUI – Netscape – IE – Firefox 14 1.3 Computer Software • Operating system • Other system software – utilities – programming language systems • Applications 15 Operating System • E.g. Windows®, Linux, Mac OS X, Unix® • Controls – the interaction of system with the user – hardware interactions • Part is usually stored on ROM, rest on hard drive – This arrangement requires booting the system 16 Some OS Responsibilities • Communicating with the user; receiving user commands • Managing allocation of memory, processor time, file system, and other resources • Collecting input from keyboard, mouse, etc. • Conveying output to screen, printer, etc. • Writing data to secondary storage devices 17 Application Software • Does the “real” work • Common application software – – – – – Word processors Desktop publishing programs Spreadsheets Presentation managers Drawing programs 18 Programming Languages • Machine Language – Most fundamental language of the computer – Unique for each processor type – Binary 0s and 1s that specify what to do • 0010 0000 0000 0100 • 1000 0000 0000 0101 • 0011 0000 0000 0110 19 Table 1.2 A Program in Machine and Assembly Language 20 High - Level Languages • Resemble human language – Java, C++, C, Pascal, FORTRAN, Ada a = a + b; • More compact and human understandable than machine language • Must be translated into machine language 21 1.4 Processing a High-Level Language Program • Set of programs used to develop software • A key component is a translator – Compiler • Examples – Java, g++, Microsoft Visual C++® • Other programs needed – Editor – Linker – Loader IDE (e.g. Eclipse) 22 Processing a Program • Editor used to enter the program – Like minimal word processor – Creates source program file • Compiler translates the source program – Displays syntax errors – Creates (usually) temporary object code file • Linker/Loader to combine object file with other object files and execute program – Creates final executable program 23 Executing a Program • CPU – examines each program instruction in memory – sends out command signals required to carry out the instruction • Special instructions used to – input data into memory for the program to use – output data to display or printer (or other device) 24 Editor used to create program Source File Compiler translates program into machine language Java .java successful unsuccessful Error Messages Other Object Files Byte Codes .class Java Runtime Environment 26 1.5 Software Development Method 1. Problem Analysis – – – Identify data objects Determine Input / Output data Constraints on the problem 2. Design – – – Decompose into smaller problems Top-down design (divide and conquer) Develop Algorithm (Desk check) • Algorithm refinement 27 Software Development Method 3. Implementation Converting the algorithm into programming language 4. Testing – – Verify the program meets requirements System and Unit test 5. Maintenance – All programs undergo change over time 28