* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
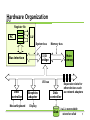
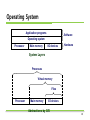
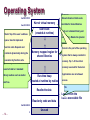
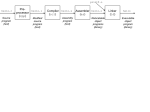
[2011-2] 시스템 프로그래밍 Class 2 : Introduction 담당교수 : 최 윤 정 2011. 8.31 Introduction Compilation Process Preprocessing Phase Compilation Phase Modifies the original C program according to the directives (#) Translates the C program into Assembly-language program Assembly Phase Transforms the Assembly-language program into Machine language programs Linking Phase Merge all the necessary object files to generate executables. 2 printf.o hello.c Source program (text) Prehello.i processor (cpp) Modified source program (text) Compiler (cc1) hello.s Assembly program (text) Assembler hello.o (as) Relocatable object programs (binary) Linker (ld) hello Executable object program (binary) 3 Hardware Organization Buses I/O Devices The system’s connection to the external world In the example, keyboards, mouse, display, disk drive Main Memory Carry bytes of information back and forth between components Temporary storage device holding both a program and the data while the processor executes the program Processor CPU interprets instructions stored in main memory PC (program counter) points at some machine language instructions in main memory Register File and ALU CPU executes very simple operations Load (from MM to Register), Store (from Register to MM), Update (Copy bytes to ALU, stores the result in a register), I/O Read (from I/O device to Register), I/O Write (from Register to I/O device), Jump (change PC value using a word extracted from the instruction), etc. 4 Hardware Organization CPU Register file PC ALU System bus Memory bus Main memory I/O bridge Bus interface I/O bus USB controller MouseKeyboard Graphics adapter Disk controller Display Disk Expansion slots for other devices such as network adapters hello executable stored on disk 5 Running “hello, world” – reading k/b CPU Register file PC ALU System bus Memory bus Main "hello" memory I/O bridge Bus interface I/O bus USB controller Mouse Keyboard User types "hello" Graphics adapter Disk controller Expansion slots for other devices such as network adapters Display Disk 6 Running “hello, world” loading CPU Register file PC ALU System bus Memory bus "hello,world\n" Main memory hello code I/O bridge Bus interface I/O bus USB controller Mouse Keyboard Graphics adapter Disk controller Display Disk Expansion slots for other devices such as network adapters hello executable stored on disk 7 Running “hello, world” - writing CPU Register file PC ALU System bus Memory bus Main "hello,world\n" memory hello code I/O bridge Bus interface I/O bus USB controller Mouse Keyboard Graphics adapter Disk controller Display "hello,world\n" Disk Expansion slots for other devices such as network adapters hello executable stored on disk 8 Caches and Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers Smaller, faster, and costlier (per byte) storage devices L1: On-chip L1 cache (SRAM) L2: L3: Larger, slower, and cheaper (per byte) storage devices L5: CPU registers hold words retrieved from cache memory L4: Off-chip L2 cache (SRAM) L1 cache holds cache lines retrieved from the L2 cache L2 cache holds cache lines retrieved from memory Main memory (DRAM) Main memory holds disk blocks retrieved from local disks Local secondary storage (local disks) Local disks hold files retrieved from disks on remote network servers Remote secondary storage (distributed file systems, Web servers) 9 Operating System Application programs Software Operating system Processor Main memory I/O devices Hardware System Layers Processes Virtual memory Files Processor Main memory I/O devices Abstractions by O/S 10 Operating System Processes Operating system’s abstraction for a running program Multiple programs can run concurrently on the same system Concurrency provided by context switch Context: State information that the process needs to run including values in PC, registers, and main memory shell hello process process Time Application code OS code Context switch Application code OS code Application code Context switch 11 Operating System Threads Execution units in a process Each thread runs in the context of the process and shares the same code and global data Easier to share data between multiple threads than processes Typically more efficient than processes 12 Operating System Virtual Memory Abstraction that provides each process with the illusion that it has exclusive use of the main memory Process’s uniform view of memory 13 Operating System 0xffffffff 0xc0000000 Kernel virtual memory User stack (created at runtime) Stack: Top of the user’s address Memory Shared Libraries: Holds code invisible to user code and data for shared libraries such as C standard library and math library. Related to dynamic space. Used to implement linking (CH 7). function calls. Expands and Kernel is the part of the operating contracts dynamically during the Heap: Expands and contracts 0x40000000 execution by function calls. dynamically at run time as a Memory mapped region for shared libraries memory. Top ¼ of the virtual memory reserved kernel. Program Code for andthe Data: result of calls to C standard library routines such as malloc Run-time heap (created at runtime by malloc) and free. Read/write data Read-only code and data 0x08048000 – 14 – printf() system that function is always resident in 0 Unused Applications are not allowed Initialized directly from the access. contents of an executable object file Loaded from the hello executable file Operating System Files A sequence of bytes. Every I/O device is modeled as a file. A network is another I/O device to O/S. 15 Conclusion A Computer system consists of hardware and system software. Processors read and interpret binary instructions stored in main memory. Storage devices that are higher in the hierarchy are faster. Can help performance optimization. Operating system kernel serves an intermediary between the application and hardware. O/S provides three fundamental abstractions: Files for I/O devices, VM for MM and disks, Processes for Processor, MM and I/O devices. Network is just another I/O device. 16