* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
Carolingian Empire wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
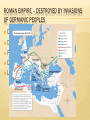
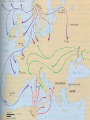
CHAPTER 13 Beginning of Medieval Europe (9, 12d, 12a) ROMAN EMPIRE – DESTROYED BY INVASIONS OF GERMANIC PEOPLES Disruption of Trade Downfall of Cities Population Shifts Decline of Learning Loss of common language FOUNDATIONS OF EARLY MEDIEVAL SOCIETY Classical heritage of Rome Christian beliefs = Unified Europe Customs of Germanic tribes INFLUENCE OF THE ROMAN CATHOLIC CHURCH Roman authority declined, while church authority grew Monasteries preserved Greco-Roman Cultural achievements Missionaries carried Christianity and Latin alphabet to Germanic tribes Pope anointed Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor – 800AD Parish Priests served religious and social needs of the people FEUDAL SOCIETY (POLITICAL ORGANIZATION) Europe in Chaos! We need PROTECTION! Fief – piece of land given from lord to his vassal, called a manor Vassals – people who serve their lord Serfs – a.k.a. peasants, people who work on fiefs Money goes up; Feudal obligations Protection goes down. Vassal – pay taxes to lord, military service Lord – protect his vassal MANORIAL SYSTEM (ECONOMY) Rigid Class structure Self-sufficient manors AGE OF CHARLEMAGNE Franks, Gallic tribe, emerge as a force in Western Europe Pope crowned the Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire = Power of the Church established in political life Roman Cultural was revived AFTER CHARLEMAGNE Son, Louis, was not a strong king Louis had three sons Lothair Charles the Bald Louis the German They fought each other Eventually divided Charlemagne's kingdom into three halves at the Treaty of Verdun Video Europe after the Fall of Rome SECTION 2 – FEUDALISM IN EUROPE New Invasions Trouble Europe Vikings Causes Overpopulation Lack of land at home Desire for free stuff Used Long Boats to raid around Europe Terrorized villages along coast Also explored Leif Ericson even reached North America around 1000 A.D. Magyars and Muslims Contributed to chaos Grabbed people to sell as slaves Video – Vikings Warriors SECTION 3 – THE AGE OF CHIVALRY Horseback – Two inventions Saddle Stirrups Knights Served their lords in return for fiefs of land Time spent in training for battle CHIVALRY Knightly code of conduct Respect for Ladies Reverence to God Loyalty to sworn lord Glory in battle and tournaments CHIVALRY CONT. Knights must maintain character standards or be punished Knights competed in tournaments to show off their skillz Warfare was terrible p.329 KNIGHTLY LITERATURE Epic Poetry in Medieval times Idealize chivalry and Knighthood Praised heroic deeds and adventures King Arthur and the Knights of the Round Table Charlemagne's battles Song of Rolan p. 330 Troubadours Sang epic songs with a lute (simple guitar) Themes of Love and Loyalty To lord To lady