* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US19746 Element 1 - cashmerescience12and13
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Multidimensional empirical mode decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
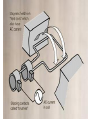
Element 1 Factors affecting quality and reliability of electronic products 1.1 Factors affecting quality are identified, their causes described, and methods of improvement outlined. 1.2 Sources that adversely affect reliability are described. 1.1 Factors affecting quality are identified, their causes described, and methods of improvement outlined. Typical factors affecting the quality of electronic products are: Interference Noise pickup Feedback Distortion User-unfriendly design Appearance User-unfriendly design Definition Design of a product which is difficult to use for intended users Typical Cause Lack of research / Incomplete analysis of product requirements / Inadequate testing / Failure to evaluate user response Method of Improvement Appearance Definition The appearance of an object is the result of a complex interaction of the light incident on the object, the optical characteristics of the object, and human perception. Typical Cause In appropriate size / colour / shape / texture / weight; Unpleasant feel Method of Improvement Interference Definition Extraneous energy, from natural or man-made sources, that impedes the reception of desired signals Typical Cause Another transmitter at the same frequency / mains frequency (50Hz) interference Method of Improvement Feedback Definition The return of a portion of the output of an active device or system to the input Typical Cause Speaker sound re-entering a microphone / coupling between the input/output circuits Method of Improvement Distortion Definition Any departure of the output signal waveform from the input signal Typical Cause Non-linearities in the devices such as a transistors and op-amps Method of Improvement Noise pickup Definition An incoherent emission from a natural or manmade source Typical Cause Lightning / Commutator noise / Ignition system noise from petrol engines Method of Improvement 1.2 Sources that adversely affect reliability are described. There are a number of sources which directly contribute to adverse reliability such as: Intermittent connections Humidity Temperature Dust and dirt Radiation Electronic component failure Mechanical component failure Electrostatic discharge Vibration Shock Corrosion Intermittent Connections Connections which spasmodically become a high resistance current path can affect the reliability significantly. Humidity High humidity can lead to a build up of moisture within equipment leading to shortcircuit paths developing and causing equipment to fail. Temperature High ambient temperatures can lead to insufficient cooling of electronic components and junction temperatures exceeding their specification, leading to component failure. Dust and Dirt Often contain carbon or other conducting material, leading to short circuits and equipment failure. Radiation Causes electrical interference, leading to distortion of analogue signals or incorrect operation of digital equipment. Electronic component failure If there is no parallel redundancy in the equipment design, component failure produces system failure. Mechanical component failure Often leads to electrical failure if: a failed mechanical joint is also an electrical connection OR the failed joint results in an open circuit. Mechanical failure can result in a broken product which works electrically but cannot be used. Vibration Vibration can lead to mechanical failure of components which leads to electrical failure and system failure. Shock Can produce sudden mechanical and electrical failure of components or connections. Corrosion Corrosion of components or connections leads to their mechanical and electrical failure. Electrostatic Discharge Produces electrical damage of semiconductor components and subsequent system degradation or malfunction. Sometimes the damage is initially undetected but produces premature failure in the component.