* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islamic Culture
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
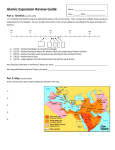
Rise of Islam The Middle East Themes in Islamic History • Islam as Religion • Islam as State & Empire • Islam as Civilization Arabia Arabia in 600 AD • Populated by various Arabic-speaking people – Bedouin - pastoral nomads organized in tribes – Agriculturalists, living either in oases in the north, or in the more fertile and thickly settled areas to the south – Intense tribal loyalties & warfare • Arab culture revered oral story telling • • Majority of Arabs followed polytheistic religions & worshipped idols – Few tribes followed Judaism, Christianity or Zoroastrianism City of Mecca was a religious & trade center – Rich mixtures of culture – Ka'aba - small temple reportedly founded by Abraham – Pilgrimage to site – Much social injustice & economic disparity Muhammad (570 – 632) • • • • • • • • • • • Born at Mecca into the powerful Quraysh tribe Orphaned at an early age & raised by uncle Illiterate but very articulate & well liked Became a successful merchant – traveled north Married older wealthy widow at 25 - Khadijah Saw a crisis in Arab society 610 AD….the divine call – Visited while meditating in cave by the Archangel Gabriel who commanded him to recite verses sent by God – Revelations continued for the next 22 years – Revelations collected in the Quran – Revelations directly related to the needs of the Arab people – First memorized the verses & passed them to his wife & close relatives – Small band of followers would memorize the recitations First converts – wife, cousin Ali, kinsman Abu Bakr Starts preaching in 612 New recruits mainly from slaves and lower classes Nocturnal journey to Jerusalem Muhammad • • • • • • 612-622 AD - in Mecca preaching and gaining followers – Seen as a trouble maker for attacking the established religion of Arabia – Attempts to assasinate him AD 622… the Hegira to city of Medina – Request to resolve dispute between rival tribes – With followers fled to neighboring city of Medina – Year 622 as the start of the Muslim calendar 622-630 AD---in Medina – Becomes leader of city – Islam becomes state religion – Develops concept of Umma - community – Mecca and Medina went to war – Unites the surrounding tribes behind him through conquest and conversion – Conflicts & suppression of Jews in Medina 630 – Mecca captured without fight – Cleansed the Kaaba of idols 632 – first Hajj or pilgrimage By his death in 632, Muhammad had managed to unite the entire Arabian peninsula Legacy of Muhammad • Believed Arabs should have a scripture like the Jews & Christians – “People of the Book” – Developed all incompensing religion • Developed concept of Ummah – Community of Allah – First attempt to create a social organization out of faith instead of tribal relationships • Vision of social justice for the Arabs – Weak & vulnerable should be protected & treated with respect • Performed the functions of prophet, lawgiver, religious leader, chief judge, commander of the army and civil head of state • Inspiration as role model for living divinely inspired life – By imitating details of his external life Muslims hoped to acquire his interior attitude of perfect surrender to God – Reproduce how he ate, washed, loved, prayed, spoke, etc. Religion of Muhammad • • • • • Islam is the religion of submission or surrender to Allah – Simple and uncompromising faith in oneness of God Muhammad did not believe he was preaching a new religion – Did not wholly reject Judaism and Christianity – Sent by God in order to complete and perfect those teachings – Accepted Abraham, Moses and Jesus as prophets – Muhammad is the messenger of God – Last in a long line of prophets Chosen by God to preach repentance and submission to God Judgment Day – Allah rewards the faithful with a paradise filled with eternal pleasure – Warns of the inevitable apocalypse & end of the world – Humanity will be forced to atone for sins – Images of heaven (oasis) & hell (desert) Belief in Predestination – Whatever happens, good and evil, proceeds from divine will Quran - Koran • Means “Recitation” – Recitation – Communicating directly with God • • • • • • • • • • Provides a guide for living as a Muslim Textbook from which practically every Muslim learns to read Arabic Revelations from God delivered through the angel Gabriel to Mohammed over 22 years Revelations came from a heavenly book containing God’s wisdom – Mother of the Book Final uncorrupted revelation of God Many parallels between Koran & Old Testament Contains 114 suras – verses – Arranged by the length of sura Contents: Theological dogma, ceremonial regulations, laws related to social, civil and criminal behavior Themes – Oneness of Allah, his attributes, the ethical duties of man, and coming retribution Quran must remain in Arabic – Translations not authentic Writing of the Quran None of Quran was written during Muhammad’s life – Still an oral scripture • Words of the Prophet at first memorized & written on parchment or clay by followers Zayd ibn Thabit – one of Muhammed’s secretaries • Began gathering the verses of the Quran soon after his death • Interviewed closest associates • Sorted into a type of order Uthman (644-656) Third Caliph – created an official and final version • Committee charged with compiling Quran in 651 • Wanted to avoid controversy • Collect and authenticate verses Strict criteria for authenticity • 2 eyewitnesses had to testify that each verses had been recorded in the presence of Muhammad • Then verified with companions of Muhammad • Approved verses amassed into single text • Uthman then ordered all other texts destroyed • Quran not altered since Religion of Islam • • • • • • • • Islam is open to all who accept its tenets Prohibition against idolatry or graven images Islam has no organized hierarchy – No religious authority, clerical elite or priesthood to act as intermediary – Mullahs (teachers) occupy positions of authority because of their knowledge of the Quran Sunna or Hadith - written collection of Arab oral traditions concerning life of Muhammad – Address issues not specifically covered in the Quran Sharia – Islamic Law – Three sources – Quran, Sunna and Ijtihad – analytic reasoning to cover locally raised issues Quran prohibits alcohol and gambling Jihad – Call for Holy War against infidels – Goal to assume political power in order to implement Islamic principles – Purpose not territorial expansion or forced conversion – Allah called for holy war to defend the faith – To die in a jihad brought salvation and entry into paradise Quran insists that there be no coercion in matters of faith The Five Pillars of Faith 1. Profession of Faith - Shahadah “There is no God but Allah (God), and Muhammad is His Prophet.” – First and last words heard – Most repeated words by Muslims – Person a Muslim once profession is repeated 2. Prayer – Salat – 13 essentials must be observed – Direction toward Mecca – 5 times a day – Call of Muezzin – Dawn, midday, mid-afternoon, sunset & nightfall – Create sense of solidarity and social equality – Body posture essential – Must use Arabic – Friday noon prayer is only mandatory public prayer for all adult males 3. Charity – Zakat – purification • Evolved out of compassion for the poor • 2.5 % of wealth expected The Five Pillars of Faith 4. Fasting - Sawm • Ramadan – based on lunar calendar – different each year • Daylight hours during month of Ramadan • Abstain from sexual intercourse 5. Pilgrimage to Kaaba in Mecca – Hajj • All those who can afford and physically fit • Ideal of equality & unity among believers • Unites cultures and ideas Women in Islam • Under Arabian pre-Islamic law of status, women had virtually no rights – No limitations were set on men's rights to marry or to obtain a divorce. • Islamic law provided women with new legal rights – Reforms affected marriage, divorce, and inheritance • Islamic law restricted the polygamy – Maximum of four wives – Women could obtain a divorce – Women could inherit and keep their own property • Marriage was no longer viewed as a "status" but rather as a "contract" • Women are separated from the company of men • Law doesn't require women to wear veils Islam After Muhammad • At death Muhammad in 632 he left no son to succeed him • Daughter Fatima • Split between Shiites and Sunnis – Great arqument over succession • Shiites – Only descendants of Fatima or her husband Ali should succeed Mohammed – Death of Husain (son of Ali) most celebrated event in Shiite calendar • Sunnis – any follower of Islam should be eligible to lead – Division political & religious – Never settled to this day • Series of Caliphs governed the Islamic State Struggle for Succession Number of conflicting parties sought to succeed Muhammad • Companions – belonged to Muhammad’s tribe or had accepted mission early • Legitimists – heir must belong to family of Muhammad – • Aristocracy of Quraysh – Umayyads – • Ali paternal cousin, husband of daughter Fatima & one of first believers Held reigns of power & wealth in pre-Islamic days Companions triumphed with selection of abu-Bakr Rashidun - Four “righteous” caliphs (632-661 AD) – All were close associates and relatives of Muhammad • Abu Bakr (632-634) Father-in-law of Muhammad and one of first believers • Umar (634-644) main military genius who carried Islam forward from the Arabian peninsula • Uthman (644-656) - empire fell into a civil war called the Fitna – In 656 Uthman is assassinated by followers of Ali • Ali (656-661) Muhammad's son-in-law and cousin – Many refused to accept Ali as a leader – Killed by assassin Umayyad dynasty claims the caliphate – Damascus capital Abbasid dynasty – 754 – seizes caliphate – al Mansur (754-775) builds new capital at Baghdad Conquest & Expansion Expansion of Islamic empire against Byzantine & Sassanid (Persian) empires Abu-Bakr –Orders jihad (holy struggle) against the "infidel" Christian or Byzantine Empire north of Arabia • Damascus becomes capital Umar • 637 – Defeated great Persian Sassanid army • 639 – Conquers Alexandria – base of Byzantine navy • 643 – Arabs to border of India Tariq ibn Zaid crossed from North Africa (Morocco) into Spain in 711 Expansion stopped in France in 732 – Charles Martel Military victories • Booty not fanaticism • No longer making war with other Arabs • Use of cavalry and camels • Remarkable mobility • High morale from religious enthusiasm Conquered peoples more open to Islam • Heavy burden of taxation • Persecution of faiths • Alien cultures The Spread of Islam Medieval Baghdad Medieval Baghdad 762 - Abbasid dynasty moved the capital of Islamic empire to the newly-founded city of Baghdad • Caliph Al-Mansur founded • Banks of the Tigris River • Known as the “Round City” • Foreign influences – Persian, Syrian & Hellenistic Baghdad capital of "Golden Age" of Islamic civilization • Magnificent architectural achievement • Muslim scholars - important contributions in the sciences, humanities, medicine, mathematics, astronomy, chemistry, and literature • Became city of museums, hospitals, libraries • World's richest & most intellectual city of the time • Believed to be largest city in the world from 775 to 935 - possibly over 1,000,000 Baghdad was destroyed by the Mongols in 1258 • Ended era of the Abbasids Medieval Baghdad Bayt al-Hikmah (the House of Wisdom) • • • • World famous center of learning Attracted scholars from all over the world Library, academy and translation bureau Translate Greek works of Aristotle, Plato, Galen, Hippocrates, Euclid, and Pythagoras • Translate Persian, Sanskrit, Syriac into Arabic • Al-Khawarizmi, the "father" of algebra Merchants played a major role in the city • From Persia, China, India, Africa & Europe • Sinbad the Sailor recounts actual voyages made by Muslim merchants Caliphal palace known as the Golden Gate or the Green Dome • Dome of audience chamber rose to 130 feet Harun al-Rashid Abbasid caliph (r.786-809) Baghdad a city of immense wealth and international significance under al-Rashid • Tribute paid by many rulers to the caliph • Used on architecture, arts & luxurious life at court Great patron of arts & sciences • Encouragement of learning, art, poetry, music • A scholar and poet himself • Invited many scholars to the kingdom • Founded first Muslim hospital Built Green Dome palace in Baghdad Fabulous court inspired the book One Thousand and One Nights • Displays of extravagant wealth • Entertainers flocked to his court: poets, wits, musicians, singers, and dancers Diplomatic relations with Charlemagne Islamic Spain • Influence on Medieval European civilization • Ummayyad Caliph • In Spain from 711 to 1492 Cordoba • Center of culture that rivaled Baghdad • Libraries, palaces, street lights, running water • Cultural center of Medieval Europe • Mosque – early vaulting like later Gothic cathedrals Creation of Islamic Civilization • Islamic civilization developed slowly – Centuries before majority of people in Syria, Mesopotamia, and Persia accepted Islam – People generally converted from self interest – Escape taxes & seek identification with ruling class • Combination of cultural influences • Arabs assimilated, adapted & reproduced the intellectual & cultural heritage of those they conquered • Arabs adopted best art, architecture, philosophy, medicine, science, literature, and government mainly from Hellenized Aramaic & Persian civilizations • Arab contribution was mainly in language and religion • Final culmination of Semitic civilization which started in the Fertile Crescent developed by Assyro-Babylonians, Phoenicians, Aramaeans and Hebrews Islamic Unity • Arabic became language of business, government & literature • Uniform enforcement of law contributed to growth of united culture • Vast trade network extended from India to the Mediterranean Rich Cultural Achievements • • • • • • Many Islamic centers of culture and science – Baghdad – Cairo – Damascus – Cordoba – Alexandria Scholarship – Produced notable scientists, astronomers, mathematicians, doctors and philosophers – Importance of reading the Qur'an produced a comparatively high level of literacy in the general populace Heirs to Hellenistic Learning – Maintained Classical learning – Translation of Greek texts - Aristotle Medicine Architecture – Mosques, Palaces & Minarets Art – Geometric patterns, calligraphy, metal work Science & Medicine Muslim scientists • Saw no contradiction between religion and laws governing natural world • Scientific method born • Utilized Classical Greek medical texts • Alchemy – beginnings of chemistry Muslim medicine • Advanced techniques & ideas • Theory that disease born through air born organisms • Study of anatomy • Vascular & cancer surgery • Study of light, lenses & physiology of eye – led to camera • Use of anesthetics • Pharmacies • Hospitals – separate disease in different wards Pioneers of Medicine Razi (865 – 925) – Rhazes in the West • Authored more than 100 books on medicine • First to diagnose and treat smallpox Ibn Sina (980 – 1037) – Known as Avicenna • Contributions in philosophy, music, mathematics, geography & literature • Utilized experimentation & observation • wrote Canon of Medicine – encyclopedia of medicine • Study of infectious disease • Main medical text for 6 centuries • Printed extensively throughout the West Mathematics • Introduced “Arabic” numerals – originally from India • Replaced Roman numerals • Included the zero – made for complex calculations • Perfected use of decimals and fractions • Invented Algebra One Thousand and One Nights Classic of world literature Stories were created over many centuries, by many people and in many styles Originally Arabian, Persian, & Indian folk tales • Collected during time of al-Rashid Best known stories: • Ali Baba, Sinbad the Sailor, and Aladdin • al-Rashid’s court frequent setting Frame story: • Efforts of Scheherezade to keep her husband, King Shahryar from killing her by entertaining him with a tale a night for 1,001 nights • Always a cliff hanger British translator – Richard Burton Architecture