* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam and the Islamic Caliphate
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
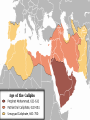
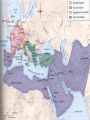
The Rise Of Islam The Life of Muhammad • • • • • • • • 570-632 A.D. Born in Mecca Belief: Message by Allah (Allah = God) Holy text became the Qu’ran (Koran) Muhammad: Founder of Islam Islam = Submission to the will of Allah Those who practice Islam are called Muslims Muhammad seeks to teach others. After three years, he had only 30 followers! • Muhammad leaves Mecca and goes to Yathrib (Medina) • Eight years later, the number increased to 10,000. • He returns to Mecca and takes over. • Converts the rest of the population. • How does Muhammad compare to Jesus? The Significance of Medina The Significance of Mecca • Mecca, Saudi Arabia • Islam's holiest city • Birthplace of the prophet Muhammad • Over a billion Muslims around the globe face Mecca in devout prayer Holy pilgrimage • The Qur’an dictates that all Muslims in good health with adequate finances must make a pilgrimage (called the Hajj) to Mecca at least once in their lifetimes. • About two million Muslims (from some 100 countries) make this religious journey each year. What are they going to see? • Mecca's sacred black Ka'bah (see photo). • Outdoor, near-cubic structure is draped in black • It housed the holy Black Stone that Muslims believe was given by heaven to the prophet Abraham. • The Ka'Bah is surrounded by the Great Mosque, which in turn is encircled by the city of Mecca. Aerial View of Mecca Basic Ethical Code of the -Five Pillars of Islam1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Belief in Allah and in Muhammad as his prophet Standard prayer five times a day and public prayer Observation of the holy month of Ramadan (the 9th month in the Muslim calendar) “Fasting” If possible, making a pilgrimage to Mecca Giving alms to the poor and unfortunate Basic Ethical Code •The Shari’ah is the Islamic system of law. Unlike the western world, the Shari’ah did not separate church and state. •Much of the guidelines came from the Qur’an. Guidelines under the Shari’ah •Muslims were forbidden to gamble, eat pork, drink alcohol, or engage in dishonest behavior •Marriages were arranged •Contacts between unmarried were discouraged •Men could have more than one wife as long as they could adequately provide for them. Islam After Muhammad • When Muhammad died, there needed to be a sucessor. • After much debate, the new leader appointed, was his father in-law, Abu Bakr • Abu Bakr was named Caliph (leader of the Islamic community) • Abu Bakr continued with jihad as Muhammad did. • According to the Qu’ran, jihad means struggle or striving in the way of (Allah). • The concept of Jihad is left up to numerous interpretations. • Jihad is often translated as holy war • Bakr will help expand the Arab Empire • He will die two years after being named caliph. • Ali, Muhammad’s son in law, was chosen as the caliph. • There was a great dispute about Ali being chosen. • Ali is the central figure at the origin of the schism that led to Shia/Sunni split. • Schism means a division of a group into opposing factions. (This is similar to the different branches of Christianity.) • Shia Muslims feel that Ali should have been the first caliph and that the caliphate should pass down only to direct descendants of Muhammad • The death of Ali: A supporter murders him, but motive is left unclear. • The next caliph: Mu’awiyah Umayyad (oo-my-ad) Who is the next leader? Sunni and Shia Muslims • Sunni Muslims are the largest denomination of Islam. • The caliph should be chosen by Muslim leaders. • Shia Muslims are second to the Sunnis in denomination. • The caliph must be a descendant of the prophet Muhammad. ISLAM OVERVIEW Muhammad & Four Caliphs Seljuk Turks • Establish a Sultan- “Holder 1. Abu Bakr of Power” 2. Umar • Turks will take over a great 3. Uthman portion of the Byzantine 4. Ali Empire Umayyad Caliphate • The Byzantine Empire will • Mu’awiyah Umayyad call for help from the West. • Move capital city from Medina to Damascus, Syria • Moors are Muslims from North Africa who settled in Spain. Ibn Sina Devised medical textbook used until 1650 in European Universities Contributions In c. 800 AD the mathematical discipline of Algebra was created. Be familiar with other Islamic contributions in the text book as well.