* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drawing an Elliptical Arc
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Architectural drawing wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Engineering drawing wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
CHAPTER 7
Drafting Geometry
Learning Objectives
• Draw parallel and perpendicular lines
• Construct bisectors and divide lines
and spaces into equal parts
• Draw polygons
Learning Objectives
• Draw tangencies
• Draw ellipses
• Solve an engineering problem by
making a formal drawing with
geometric constructions from an
engineer’s sketch or layout
Drafting Geometry
• Geometric constructions
• Requires a basic understanding of
plane geometry
• Important theory even when using
CADD
Characteristics of Lines
• Straight line segment
• Line of any given length
• Curved line
• Arc with a given center and radius
• Irregular curve without a defined radius
Characteristics of Lines
• Parallel lines
• Perpendicular lines
• Intersecting lines (shown)
Angles
• Formed by the intersection of two lines
• Sized in degrees (°)
• One degree (°) = 60 minutes (')
• One minute (') = 60 seconds (") in one
minute. 1°= 60', 1' = 60"
Angles
Triangles
• Equilateral
• Isosceles
• Scalene
Right Triangles
• Two internal angles equal 90°when
added
• Hypotenuse
Quadrilaterals
• Sum of the interior angles = 360°
• Parallelograms
Regular Polygons
• Equal sides
• Equal internal angles
• Common geometric shape on drawings
Regular Polygons
Name
Number of Sides
Triangle
3
Square
4
Pentagon
5
Hexagon
6
Octagon
8
Regular Polygons
• Calculating internal angles
• 12-sided polygon example:
Divide
360° (360° in a circle) by 12 (360 ÷
12 = 30°)
30° between each side of a 12-sided polygon
Polyhedrons
• Regular polyhedrons
• Surfaces referred to as faces
Prisms
Pyramid Prisms
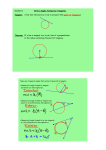
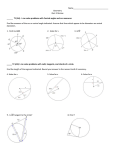
Circles
Arcs
Ellipses
Spheres
Tangents
Drawing Lines
• LINE command
• Common accurate construction
techniques:
• Cartesian coordinate system
• Geometric constraints
• Dimensional constraints
Drawing Circles
• CIRCLE command
• Center and point on the circumference:
•
•
•
•
•
•
radius
Center point and radius value
Center and point past the circumference:
diameter
Center point and diameter value
Two opposite points on the circumference:
diameter
Three points on the circumference
Tangent to objects
Drawing Arcs
• ARC command
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Start point, point along the arc, and end point
Center point, start point, and end point
Start point, end point, and radius value
Start point, point along the arc, radius, and
length or chord length
Start point, point along the arc, center, and
length or chord length
Start point, center point, and included angle
Start point, end point, and tangent direction
Tangent to objects
Drawing Parallel Objects
•
•
•
•
•
•
PARALLEL object snap
Grid and grid snap
Orthogonal mode
AutoTrack
OFFSET command
PARALLEL geometric constraint
Drawing Concentric Circles and
Arcs
• CENTER object snap
• OFFSET command
• CONCENTRIC geometric constraint
Drawing Perpendicular Lines
•
•
•
•
•
PERPENDICULAR object snap
Grid and grid snap
Orthogonal mode
AutoTrack
PERPENDICULAR geometric constraint
Constructing a Perpendicular
Bisector
Bisecting an Angle
Transferring a Triangle to a New
Location
Dividing a Line or Space into Equal
Parts
• DIVIDE or similar command
• MEASURE or similar command
• Measure the line or space, calculate the
measurement between each division, and
offset the calculated measurement
• RECTANGULAR PATTERN, ARRAY, or
similar command
• Graphic pattern command
Drawing Regular Polygons
• POLYGON command
• EQUAL geometric constraints to each
side
• Multiple equal angular dimensional
constraints
Drawing a Triangle Given Three
Sides
• LINE command and construction based
on three sides
• POLYGON command, three sides
• Geometric and dimensional constraints
based on three sides
• Triangulation
Constructing a Right Triangle
Given Two Sides
• Draw a side perpendicular to the other
side; connect the ends to form the
hypotenuse
• PERPENDICULAR geometric constraint
establishes right angle, dimensional
constraints define sides
Right Triangle Given One Side and
the Hypotenuse
Constructing a Square or
Rectangle
• LINE command and construction based
on equal sides and four 90° angles
• POLYGON command, four sides
• RECTANGLE command
• Geometric and dimensional constraints
based on equal sides and four 90°
angles
Drawing Tangent Arcs
• ARC command from the center and
points of tangency
• FILLET or similar command
• Fillets, rounds, other tangent arcs
• TANGENT geometric constraint
Drawing a Line Tangent to a Given
Circle
• Specify know points of tangency
• TANGENT object snap
• TANGENT geometric constraint
Drawing a Circle Tangent to
Existing Objects
• CIRCLE command with tangent option
Tangency Design and Drafting
Example
Tangency Design and Drafting
Example
Drawing an Ogee Curve
Constructing an Ellipse
• ELLIPSE command
• Center and one endpoint for each axes
• Major axis or minor axis, and distance
•
•
from the center to the endpoint of the
other axis
Major axis and ROTATION or similar option
Dimensionally constrain the major and
minor axes
Drawing an Elliptical Arc
• ELLIPSE command
• ELLIPSE ARC or similar command with
an ELLIPTICAL ARC or ARC option