* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 02_Buddhism - The Huntington Archive
Yiqiejing yinyi (Xuanying) wikipedia , lookup
Relics associated with Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist cosmology of the Theravada school wikipedia , lookup
Pratītyasamutpāda wikipedia , lookup
Buddhas of Bamiyan wikipedia , lookup
Four Noble Truths wikipedia , lookup
Noble Eightfold Path wikipedia , lookup
Faith in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and violence wikipedia , lookup
Wat Phra Kaew wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist texts wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Buddha-nature wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Nirvana (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Abhisamayalankara wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Persecution of Buddhists wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist meditation wikipedia , lookup
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Gautama Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Myanmar wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
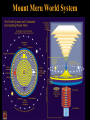
Review: Vedic /Upanishadic Traditions VEDIC TRADITION: Vedic Cosmology Vedic Gods Varna UPANISHADIC TRADITION: Upanishadic Ideas Universalistic Ideas: Brahman/Atman Samsara kalpa Brhadaranyaka Upanishad: “As he has acted, as he has lived, so he becomes; He who has done good is born again as a good one; He who has done evil, is born again as an evil one” Heterodox Religions: Jainism and Buddhism • Against the Vedic ideas, especially supremacy of priesthood, varna system, materalism of Vedic ritual • Non-Theistic • Non-Violence and equality • Upanishadic ideas: contemplation and questioning • Path of renunciation (pre-Vedic ideas) • Nastiks = deniers [of the Vedic tradition] • Astiks = believers [of the Vedic tradition] Buddhism Presuppositions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. SAMSARA: endless cycle of rebirth and deal KARMA: “action” KALPA: cyclical time of world cycles MAYA: illusion Soteriology: a release from the painful cycles by attaining enlightenment. Upanishadic Ideas: 1. Unity: universal and individual 2. Renunciate / ascetic tradition 3. Emphasis on SELF The Buddha “Founder” • historical figure born in 500 BCE • as Prince Siddhartha of the Shakya clan in Lumbini, Nepal • After enlightenment became known as the BUDDHA “one who has the knowledge” • also known as SHAKYAMUNI, “sage of the Shakya” The Buddha • teacher, NOT a god • notion of past Buddhas before him (8 Buddhas) • his life and events serve as paradigm for ALL Buddhists • All Buddhist beliefs in existence before Shakyamuni The Life of the Buddha Four Major Events as Paradigm 1. 2. 3. 4. Birth Enlightenment (bodhi) First Teaching “Turning the Wheel of Dharma” Death (nirvana) Birth of the Buddha Lumbini, Nepal Birthplace of Shakyamuni Buddha Fasting Buddha, 1st century CE Enlightenment at Bodhgaya Temple of Enlightenment, Mahabodhi Temple, Bodhgaya Enlightenment of the Buddha: Victory over Mara (death) • attained Bodhi “knowledge • Buddha: “one who has the knowledge •“Earth-touching gesture” : -earth-goddess as witness First Teaching at Sarnath, India: Turning the Wheel of Dharma Teaching the Dharma: :Turning the Wheel of Law” Four Noble Truths: 1. 2. 3. 4. Life is suffering Desire is the cause of suffering The solution is to stop having desire The way to stop desire is to follow the Buddhist Dharma (path) (8-Fold Path) : faith / practice : selfless action : ethical behavior Three Jewels: 1. Buddha (Teacher) 2. Dharma (Teaching) 3. Sangha (Community) Buddhist Teachings (Dharma) 1) Altruistic action: Having complete, unselfish compassion for others and acting on that compassion. Making continuous effort to seek advancement and to aid others 2) Yogic Meditation: Seeking through concentration and mindfulness the various types of knowledge that led to the Buddhist attainment 3) Detachment: Becoming a beggar or an ascetic in order to detach oneself from all desires. The Death of the Buddha: Nirvana • Ending the cycle of samsara Relic Cult in Buddhism: Worship and Pilgrimage 1. Bodily Relics of the Buddha STUPA Buddhist Community Buddhist Sangha: •Monastics: Monks / Nuns •Lay Commmunity: Male / female Buddhist Texts: •Monastic behavior: vinaya •Buddhist philosophical treatises and commentaries Buddhist Worship, Ritual, and Art • Communicating the key points of religion through symbols • Emphasizing faith in religion • Art begins around the 3rd century BCE Buddhist Cosmology: Mount Meru System Buddhist World System: 1. Sacred Mountain: imagined space 2. Fundamental in Buddhist philosophy and art 3. Understanding that is critical in Buddhist thought Web reference: www.huntingtonarchive.osu.edu (Circle of Bliss) Mount Meru World System Mount Meru World System Stupas as Mount Meru World System Tibet Nepal Japan Yogin and Mt. Meru Yogin and Heart-Mind Buddhist Vehicles (Yana) •Hinayana “Little Vehicle” Shrakayana: Vehicle of the Hearers Theravada: Path of the Elders Pratyeka-buddhayana: Vehicle of the Lone Buddhas Ideal: Arhats •Mahayana “Great Vehicle” Ideal: Bodhisattva (lit. “Enlightenment Beings” or Beings destined for Enlightenment) •Vajrayana “Adamantine/Diamond Vehicle” • best suited for the Kali Yuga: efficious/dangerous Ideal: Mahasiddha (crazy yogin)