* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hinduism and Buddhism
Relics associated with Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Pratītyasamutpāda wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Wat Phra Kaew wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist texts wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist cosmology of the Theravada school wikipedia , lookup
Four Noble Truths wikipedia , lookup
Buddha-nature wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Gautama Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Nirvana (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Noble Eightfold Path wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
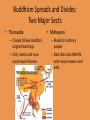
Hinduism and Buddhism Chapter 3 Section 2 The Beliefs of Hinduism Develop • No single founder and no single sacred text – Many gods and goddesses and practices Siva, god of destruction Basic Hindu Beliefs 1. One force underlies everything – Brahma 2. Sacred texts reveal Hindu Beliefs – The Vedas Brahma 3. Achieving Moksha is the Goal of Life – This is union with Brahma – To achieve must free yourself from selfish desires Karma and Dharma • Karma = all actions of a persons life that affect his or her fate in the next life • Reincarnation– Different classes • Dharma = the religious and moral duties of an individual – Pacifist The Caste System Shapes India • Castes are social groups into which people are born and which can rarely be changed. – Caste system guided everything – Strive for better class in next life – Preserved social order Key Teachings of Buddha • Arose in the 6th Century B.C. • Founded by Siddhartha Gautama, known as Buddha or “Enlightened One” From Boy to Buddha • Born a prince and spoiled and sheltered • Doesn’t witness suffering and death until age 29 • Meditated under at tree until he understood the mystery of life The Four Noble Truths 1. All life is full of suffering, pain, and sorrow 2. The cause of suffering is non-virtue, or negative deeds and mindsets such as hatred and desire 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome non-virtue 4. The way to overcome non-virtue is to follow the eightfold path Eightfold Path • • • • Right views Right aspirations Right speech Right conduct • • • • Right livelihood Right effort Right mindfulness Right contemplation Nirvana • Nirvana is the ultimate reality, the end of the self and a reunion with the Great World Soul • No worshiping of Siddhartha or his image • Often viewed as philosophy not a religion. Buddhism Spreads Beyond India • The Tripitaka, collection of Buddha’s teachings • Buddhism spreads to much of Asia, is little practiced in India today • Hinduism absorbed Buddhist beliefs and Buddha Buddhism Spreads and Divides: Two Major Sects • Theravada – Closely follows Buddha’s original teachings – Only monks and nuns could reach Nirvana • Mahayana – Made for ordinary people – Describes and afterlife with many heavens and hells Compare and Contrast Poster • Create a poster that compares and contrast Hinduism and Buddhism – – – – – – Include when they began How they began Their beliefs and practices Locations Changes to the religions Any other important information that you feel should be shared – Include a picture to go with each religion















![Buddhism[1]. - Mr. Fellens` World History Honors](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006442421_1-4b4dd9563a9db6afc434e94f46285d75-150x150.png)