* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
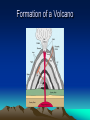
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes • An earthquake is the shaking and trembling that results from the sudden movement of part of the Earth’s crust. • The most common cause of earthquakes is faulting. During faulting, energy is released. Rocks continue to move until the energy is used up. Seismic Risk Map of the U.S. San Andreas Fault • The San Andreas fault extends 960 km from Mexico to the north of California. • The land to the west is moving north. The land to the east of the fault is moving south. All the rocks do not move at the same time so earthquakes occur in one area and then another. San Francisco Quake • In 1906, movement along the San Andreas fault caused an earthquake in San Francisco. Tsunamis • Earthquakes which occur on the ocean floor produce giant sea waves called tsunamis. Tsunamis can travel at speeds of 700 to 800 km per hour. As they approach the coast, they can reach heights of greater than 20 meters. Focus • Most faults occur between the surface and a depth of 70 kilometers. • The point beneath the surface where the rocks break and move is called the focus. The focus is the underground origin of an earthquake. Epicenter • Directly above the focus, on the Earth’s surface is the epicenter. Earthquake waves reach the epicenter first. During an earthquake, the most violent shaking is found at the epicenter. Seismic Waves • There are three main types of seismic waves. • Primary • Secondary • Surface Primary Waves • Seismic waves that travel fastest are P waves. They travel through solids, liquids and gases. • They move at different speeds depending on the density of the material through which they are moving. As they move deeper in the Earth they move faster. • P waves are push-pull waves. Secondary Waves • Seismic waves that do not travel through the Earth as fast as P waves do are called secondary or S waves. • S waves travel through solids but not liquids or gases. • S waves cause particles to move from side to side. They move at right angles to the direction of the wave. Surface Waves • The slowest moving seismic waves are called surface waves or L waves. • L waves originate on the Earth’s surface at the epicenter. They move along the surface the way waves travel in the ocean. The Earth’s surface moves up and down with each L wave. • L waves cause most of the damage. The Seismograph • Invented in 1893 by John Milne, a seismograph detects and measures seismic waves. • A weight attached to a spring remains nearly still even when the Earth moves. A pen attached to the weight records any movement on a roll of paper on a constantly rotating drum. The drum moves with the Earth and affects the line. Seismologists • Seismologists study earthquakes. They can determine the strength of an earthquake by the height of the wavy line recorded on the paper. • The seismograph record of waves is called a seismogram. • The Richter scale is used to calculate the strength of an earthquake. The Richter Scale • The amount of damage created by an earthquake depends on several factors. • The earthquake’s strength • The kind of rock and soil that underlie an area • The population of the area • The kind of buildings in the area • The time at which the earthquake occurs Magnitude & Intensity • Magnitude and Intensity measure different characteristics of earthquakes. Magnitude measures the energy released at the source of the earthquake. Magnitude is determined from measurements on seismographs. • Intensity measures the strength of shaking produced by the earthquake at a certain location. Intensity is determined from effects on people, human structures, and the natural environment. Predicting Earthquakes • Scientists have identified warning signals the help predict earthquakes with greater accuracy. • Often changes occur in the speed of P and S waves before an earthquake occurs. • Sometimes slight changes in the tilt of the Earth’s surface can be detected. • Some scientists believe animals behavior is affected. Formation of a Volcano Magma Deep within the Earth, under tremendous pressure and at great temperatures, rock exists as a hot liquid called magma. This molten rock is found in pockets called magma chambers. Lava • When the magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. The place in the Earth’s surface through which magma and other materials reach the surface is called a volcano. In some places, lava can build up to form a cone-shaped mountain. • The opening from which lava erupts is the vent. Volcanoes often have more than one vent. Dark-Colored Lava • There are four types of lava. • One is dark-colored and contains a lot of water. This is rich in iron and magnesium and cools to form igneous rocks such as basalt. This lava is thin and runny and most tends to flow. The islands of Hawaii and Iceland were formed by many lava flows. Light-Colored Lava • The second type of lava is light in color. This lava, contains little water and is rich in silicon and aluminum. Light-colored lava causes explosive eruptions. Silicon tends to harden in the vents and form rocks. Steam and new lava build up under the rocks. When the pressure becomes great, a violent explosion occurs. When this type of lava cools it form the igneous rock, rhyolite, which resembles granite. Combination Lava • The third type of lava has a chemical composition similar to that of both the dark-colored type and the light-colored type. Different varieties of igneous rocks in the Earth’s crust, such as andesite, are form from this type of lava. Gaseous Lava • The fourth type of lava contains large amounts of gases such as steam and carbon dioxide. When this lava hardens, it forms rocks with many holes in them, due to gas bubbles. Pumice and scoria are igneous rocks formed from this type of lava. Volcanic Eruptions • During volcanic eruptions, many rock fragments are blown into the air. The smallest particles are called volcanic dust. (less than 0.25 mm) • Volcanic Ash ( 0.25 -5mm) falls to the Earth and forms small rocks. • Volcanic bombs (a few cm to several meters) are molten and harden as they travel through the air. Types of Volcanoes • Different types of volcanic eruptions form different types of volcanoes. • Cinder cones • Shield volcanoes • Composite volcanoes Three Types Cinder Cones • Volcanoes made mostly of cinders and other rock particles that have been blown into the air are called cinder cones. Cinder cones form from explosive eruptions. Because the material is loosely arranged, the cones are not high. The have a narrow base and steep sides such as Paricutin in Mexico. Cinder Cone Volcano Shield Volcanoes • Volcanoes composed of quiet flows are called shield volcanoes. Because it is rummy, the lava flows over a large area. After several eruptions, a dome-shaped mountain is formed such as Mauna Loa (4km over sea level) in the Hawaiian Islands. Shield Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes • Volcanoes built up of alternating layers of rock particles and lava are called composite volcanoes. During the formation of a composite volcano, a violent eruption first occurs, hurling volcanic bombs, cinder and ash out of the vent. Then a quiet eruption, produces lava flow that covers the rock particles. After alternating eruptions, a cone-shaped mountain forms such as Mount Vesuvius. Mount Vesuvius Mount Vesuvius • Images of victims in eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. Most died as a result of suffocation. Composite Volcano Crater • There is often a funnel-shaped pit or depression at the top of a volcanic cone. This pit is called a crater. If the crater becomes very large as a result of the collapse of its walls, it is called a caldera. A caldera may also form when the top of a volcano explodes or collapses. Volcanic Crater Volcanic Activity • Volcanoes are rather unpredictable . Some erupt regularly, others have not erupted in modern history. Scientists classify them as active, dormant or extinct. Active Volcanoes • An active volcano is one that erupts whether continually or periodically such as Mount Katmai in Alaska and Mount St. Helens in the Cascade Range. Dormant Volcano • A volcano that has been known to erupt within modern times but is now inactive is classified as a dormant volcano. Mount Rainier in Washington state are example of dormant volcanoes in the United States. Extinct Volcano • A volcano not known to have erupted within modern history is classified as an extinct volcano. They have been worn away almost to the level of their magma chamber. Scientists can be wrong. Mount St. Helens was considered to be dormant but erupted after long periods of inactivity. Volcano and Earthquake Zones • Most major earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in three zones of the world. Scientists believe that there is a great deal of movement and activity in the Earth’s crust in these three zones. Ring of Fire • One major earthquake and volcano zone extends nearly all the way around the edge of the Pacific Ocean. This zone goes through New Zealand, the Philippines, Japan, Alaska and along the western coasts of North and South America. The San Andreas fault is part of this zone. Mediterranean Zone • A second Major earthquake and volcano zone is located near the Mediterranean Zone and extends across Asia into India. Many countries in the zone, including Italy, Greece and Turkey, have violent earthquakes. Many volcanic eruptions also occur in this zone. Mid-Atlantic Ridge Zone • The third major earthquake and volcano zone extends through Iceland and to the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. There is under the ocean a long range of volcanic mountains called the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Range. Scientists believe that the volcano and earthquake activity are due to the formation of new parts of the Earth’s crust along the ridge. The volcanic island of Iceland is part of this zone. Earthquake Belts Types of Volcano * According to Activity: a. Active b. dormant (inactive) c. extinct * According to Eruption a. quiet b. explosive/violent c. intermediate * According to Shape a. cinder b. shield c. composite