* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
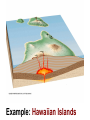
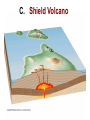
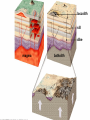
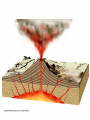
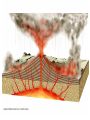
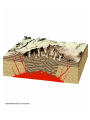
Eruptions and Forms of Volcanoes 10.1 Volcanoes and Earth’s Moving Plates • Most active volcano: Kilauea Located in Hawaii • Magma formed: Heat and pressure cause rock to melt • What causes magma up? It is less dense than surrounding rock. Divergent boundaries: plates move apart Ex: Mid Atlantic Ridge Convergent boundaries: plates move together Ex: Himalayas Pacific Ring of Fire- the area around the Pacific Plate where earthquakes and volcanoes are common Hot spot- areas in the mantle that are hotter than their surroundings Ex: Hawaiian Islands, Yellowstone National Park 10.2 Energy from Earth How does geothermal energy produce electricity? • Heat and energy from magma is used to boil water to produce steam used to generate electricity. Used in: California, Nevada, Utah, Hawaii 3 benefits of using geothermal energy: 1. Reduction in oil spills on coastlines 2. No mine waste or radioactive waste 3. Reduction in pollutants from burning fossil fuels 2 types of geothermal energy: • Magma- molten rock deep inside Earth • Hot dry rock (HDR)- water is pumped into the cracks in rock- heated then used to create steam • Which type is more available? Hot dry rock Why? Temperatures increase with depth into Earth • Which type of geothermal energy produces fewer carbon dioxide emissions? Hot dry rock • Why is HDR not used more? It is too expensive 1. 2 important factors that determine whether a volcano will be explosive or quiet. 1.) the amount of gases trapped in magma. 2.) the composition of the magma. 2. Basaltic magmas generally produce quiet eruptions. Why? Basaltic magma contains less silica and is less viscous (sticky). Example: Hawaiian Islands 2. Granitic magmas generally produce explosive eruptions. Why? Granitic magma contains more silica and is more viscous (stickier). Example: Mount Saint Helens Another factor that causes granitic magma to be explosive is the high water vapor content. 3. Andesitic magma has medium silica content (medium viscosity) Andesitic volcanoes are explosive. A. Composite (stratovolcano) B. Cinder Cone C. Shield Volcano laccolith sill dike magma batholith 1. Batholith – largest intrusive rock bodies. (greater than 100 km) How? Form when a large plume of magma cools underground. dike – magma squeezes into a vertical crack. sill – magma squeezes between horizontal rock layers. Volcanic neck – weathering & erosion remove the sides of a volcano leaving the solidified vent. 5. Caldera – when the top of a volcano collapses after a large eruption.