* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LAYERS OF THE EARTH
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
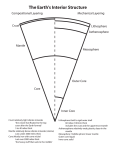
LAYERS OF THE EARTH Layers in Order 1. Crust 2. Mantle Lithosphere Asthenosphere 3. Lower Mantle 4. Outer Core 5. Inner Core Crust The Earth’s crust is like the skin of an apple. It is very thin compared to the other three layers. The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called plates. 5 to 25 miles thick and up to 1,600 F Two types of crust Oceanic and Continental Crust Cont.… Lithosphere Rigid outer layer of the crust Part of the crust/mantle Asthenosphere (part of the mantle) Solid to semi-solid rock layer The crust and plates glide on the asthenosphere Mantle Upper Mantle The mantle is the largest layer of the Earth. Consists of crystalline formations Asthenosphere is located above the mantle 1,800 miles thick and up to 8,000 F Lower Mantle Abundant in the following elements Silicon, Magnesium and Oxygen Outer Core 1,400 miles thick and up to 11,000 F Liquid Layer Spins around the Inner Core Causes the Earth’s Magnetic Field Made of… Liquid Iron and Nickel Is very dense Inner Core Solid Metal Temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move or melt. 800 miles thick and up to 13,000 F Made of.. Iron, Nickel and a few other metals