* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes
Lōʻihi Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
David A. Johnston wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
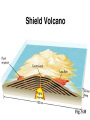
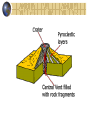
Volcanoes Chapter 8 Section 2 Class Outcomes Describe a volcano Name and describe the 4 types of volcanoes Differentiate between Pahoehoe and Aa lava Volcano Area where magma and gases are released to the Earth’s surface. Area where magma becomes lava Magma = under surface Lava= above surface Have circular shaped openings called craters Release Tephra, or solid lava, that enters the air during an eruption. Subduction Zone Volcanoes Oceanic plate dives under and melts. The newly formed magma rises to the surface and creates a volcano. 4 types of volcanoes Shield Volcanoes Cinder Cone Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Fissure Eruptions Shield Volcanoes Made from basaltic lava Thin and easy flowing “pahoehoe” Gradually sloping sides Broad/ largest volcanoes on earth Hawaiian Islands/Iceland Mauna Loa Cinder Cone Volcanoes Short in height (less than 300m) Made of tephra Violent eruptions from gas buildup Lava and gas shoot high in the air and cool to form volcano Short eruption time Composite Volcanoes Steep sided mountain Composed of alternating layers of basaltic lava and tephra Explosive eruptions followed by lava flows Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Ranier, Mt. Shasta Composite = pyroclastic flows Hot gases and ashes released at the beginning of a composite eruption 2000 degrees Fahrenheit Up to 450 miles/hour Deadliest event of a composite eruption Pyroclastic Flow Composite = “Lahars” Mud Flows caused by the super heating of glaciers on the top of these high mountains. Water + Ash = Lahar 2nd deadliest aspect of these giants. Mt. Shasta, California Fissure Eruptions Basaltic lava flows from cracks in the earth’s crust Thin and flows easily Form flat landforms known as lava plateaus/flood basalts. Volcano Tour on Google Earth tour Fissure Eruption, Kilauea Volcano field, Hawaii “Pahoehoe vs. Aa” Pahoehoe lava Thin and flows easily Aa lava Thick and chunky and doesn’t flow, but breaks apart as it moves. ? Aa ? Pahoehoe What kind of volcano would be the best to have in your backyard? Extinct • Have no magma chamber or source. Active • Have regular, predictable eruptions that never gain strength. Dormant • Have irregular, unpredictable eruptions and can be very catastrophic in strength. Enjoy the Show Mountains of Fire