* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internal Forces that Shape the Earth (Plate Actions)
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Sediment Profile Imagery wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
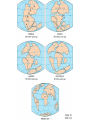
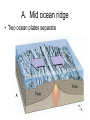
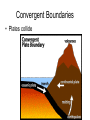
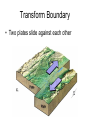
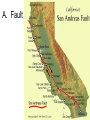
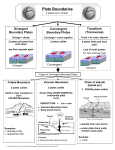
Internal Forces that Shape the Earth (Plate Actions) Plate Tectonics • Continental Drift – plates move slowly across upper mantle • “Pangaea” – supercontinent existed 250 million years ago Divergent Boundary • Plates separate / spread apart A. Mid ocean ridge • Two ocean plates separate B. Rift Valley • Two land plates separate Convergent Boundaries • Plates collide A. Mountains • Two land plates collide B. Island Chains • Two ocean plates collide C. Ocean Trench and Mountains • Land and ocean plates collide Transform Boundary • Two plates slide against each other A. Fault V. Earthquakes and volcanoes form along plate boundaries External Forces that Shape the Earth Weathering • The breaking down of rock into sediment Physical Weathering Chemical Weathering Erosion • The carrying away of sediment A. Water is the greatest agent of erosion B. Wind C. Glaciers / Ice Landforms 1. Created by tectonic processes 1. Mountains, valleys 2. Created by erosion 1. Plateau, plains 3. Created by sediment deposition 1. Sand dune, floodplain Most regions have a combination of all three types Example: Mountain range formed by tectonic activity. Erosion forms deep valleys between the mountains. Sediment eroded from the mountains is deposited at the mountains’ bases. Creates an alluvial fan. Alluvial fan: fan-shaped deposit of mud and gravel often found at the base of mountains. Stream erodes the sediment in the alluvial fan and carries them to a river mouth. Sediment moves into the ocean and sinks, or it may accumulate and build a delta.