* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INSIDE THE EARTH The Earth is made up of several layers that
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
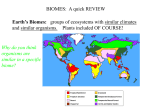
INSIDE THE EARTH The Earth is made up of several layers that have different characteristics - Core: center of the Earth made up of hot iron mixed with other metals and rock - Mantle: layer of hot, dense rock * magma can be found in the mantle and often flows to the surface during volcanic eruptions * Once magma reaches the surface, it is called lava - Crust: Earth’s upper layer consisting of a thin rocky shell that forms the surface SHAPING THE EARTH’S SURFACE - Forces acting both inside and outside the Earth work to change the Earth’s surface - Plate tectonics: theory of how the continent’s were formed and why they move o Continents sit on plates that move which is known as continental drift o Only moves 1 ot 7 inches per year - When plates meet many things can happen o Plates may collide usually causing mountains o When continental plates and ocean plates collide, earthquakes may occur o Plates may slide along one another, they create faults WEATHERING • Weathering is when water and ice, chemicals, and even plants break rocks apart into smaller pieces • Erosion is when water, wind, and ice can move away weathered rock – Running water, ocean waves, wind and giant moving glaciers may cause erosion THE WATER PLANET - Water covers about 70% of the planet, but only some of the water is usable - 97% of the world’s water is salt water making only 3% of the water is usable - Much of the freshwater is frozen in ice that covers the polar regions - The total amount of water in the world does not change and moves constantly in a process called the water cycle o Water goes from the oceans, to the air through evaporation, to the ground through precipitation, and back to the oceans through runoff EFFECTS OF THE CLIMATE - Sun – movement of air and water helps distribute the sun’s heat evenly around the Earth - Prevailing winds – warm air from the Tropics moves towards Poles and colder air from the Poles moves towards the Equator Trade winds – east to west between the Tropics Westerlies – west to east between Tropics and 60 degrees latitude - Ocean currents can carry warm water to higher latitudes bring with it a mild climate - Rain shadows block rain from reaching interior regions, usually found near the ocean CLIMATE ZONES - Climate zones are similar patterns of temperature and precipitation - Climate zones include biomes which are areas that include particular kinds of animals and plants that have adapted to the conditions there Biomes include deserts, tundra, forests, grasslands, and aquatic EFFECTS OF THE CLIMATE - Ocean currents can carry warm water to higher latitudes bring with it a mild climate - Rain shadows block rain from reaching interior regions, usually found near the ocean CHANGING CLIMATE Global warming - The increase of the Earth’s average surface temperature due to a build-up of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse effect - The buildup of certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that retain the Sun’s warmth