* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17 Study Guide Answers
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
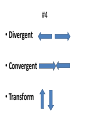
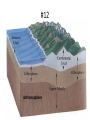
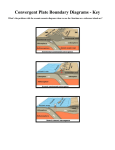
Chapter 17 Study Guide Answers #1 • Pangaea #2 • 1. Puzzle-like fit • 2. Widespread plant • 3. Animal fossil • 4. Climate clues (glaciers) • 5. Rock clues (similar mountains) #3 • Oceanic and continental • Oceanic and oceanic • Continental and continental will not have subduction. #4 • Divergent • Convergent • Transform #5 • Divergent- Mid-ocean ridges • Convergent (without subduction)- Mountains • Convergent (with subduction)Volcanoes, volcanic islands, and deep-sea trenches • Transform- Earthquakes #6 • Laurasia #7 • Gondwanaland #8 • The continents drifted apart to their current locations. #9 • Hot rising • Cool sinking • Circular motion #10 • When a oceanic plate goes under another oceanic plate of a continental plate. It is a type of convergent boundary. #11 • Younger crust is in the middle • Older crust is on the outside • Divergent Boundary #12 Asthenosphere #13 • The Atlantic Ocean is expanding because 4 plates form a divergent boundary in the middle of the ocean. This is causing the seafloor to spread apart. The Pacific Ocean is shrinking because the Pacific Plate is surrounded by convergent plate boundaries that have subduction. Basically the Pacific Ocean is being consumed. #14 • Renewable- a natural resource that can used over and over without depleting its supply. Ex. hydropower, solar, wind, biomass, and geothermal. • Nonrenewable- a resource that exists in the Earth’s crust in a fixed amount that takes a long time to be replaced. Ex. Uranium, petroleum (oil), natural gas, propane, and coal. #15