* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download n OceansShorelines
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Sea level rise wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
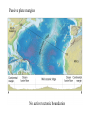
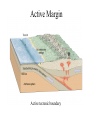
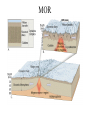
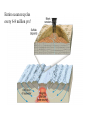
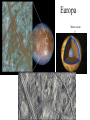
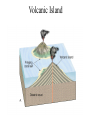
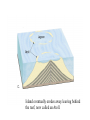
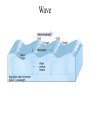
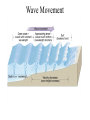
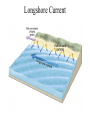
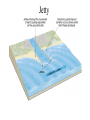
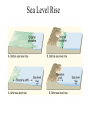
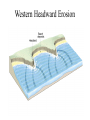
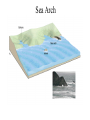
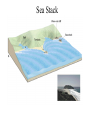
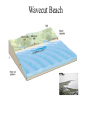
Passive plate margins No active tectonic boundaries Continental Shelf Shelf: - avg 50 miles wide and 425 ft deep - gradient of 1/10 of one degree (10 ft/mile) - shelves represent 7.5 % of the oceans area. - usually contain important mineral and petroleum deposits & fish. - evidence of sea level change - drilling & dredging has produced remains of animals abundant during the last ice age when sea levels were much lower. - usually consists of sediment washed off continent by rivers/streams Slope: - leads into deeper water, steeper gradient - avg 370 ft/ mile - marks the true edge to a continent Rise: - slope merges into a more gradual incline - gradient of 20-40 ft/mile - rise may extend for a hundred miles or more into the deeper ocean - consists of sediment moved downslope from the shelf to the deep ocean - sediment delivered here by turbidity currents moving down the slope, which follow submarine canyons Active Margin Active tectonic boundary Trenches Show us the location of subduction zones MOR Pillow Basalts Entire ocean recycles every 6-8 million yrs! Hydrothermal Sea Vents Bacteria oxidize H2S (ingest it) chemically. Independent of the sun. Chemical photosynthesis. Tube worms eat bacteria, clams, fish eat tube worms, etc. Unique ecological system on our planet -- doesn’t need the sun’s heat. QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. Europa Warm ocean Volcanic Island Subsidence plus erosion; barrier reef continually builds and remains in the same place. Barrier Reefs Island eventually erodes away leaving behind the reef, now called an Atoll. Atolls Wave Wave Movement Tsunami Longshore Current Beach Storm Response Summer: No storms. Steep beach. Winter: Storms interact with dunes, move sand offshore onto bars. Flat beach, wavecut dunes. Bars march back up to shore and dock onto beach over period of days or months, forming steep beach. Barrier Islands Tidal Channel Baymouth Bar Jetty Groin Field Seawall Seawall Erosion Seawall Erosion Prereplenishment Postreplenishment Sea Level Rise Western Headward Erosion Wavecut Cliff Sea Arch Sea Stack Wavecut Beach