* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Structure of the Earth
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
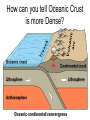
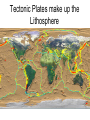
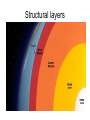
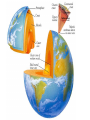
The Structure of the Earth 3 Composition Layers: Based on what the layer is made of Compositional Layers of Earth 1. Crust • Outer layer – rigid rock • Two types: –Continental Crust (thicker) –Oceanic Crust (thin and more dense) How can you tell Oceanic Crust is more Dense? 2. Mantle • Contains 67% of Earth’s Mass • Made of solid rock that is able to flow. 3. Core • Made mostly of Iron and other very dense materials. 5 Structural Layers of the Earth: based on phase or what it’s like 1. Lithosphere • “Rock Sphere” • Outermost rigid layer • Divided into pieces called tectonic plates • 15-300 Km thick • The least dense of Earth’s layers. Tectonic Plates make up the Lithosphere 2. Asthenosphere • “Weak Sphere” • Soft layer of mantle. Low density solid rock that flows very slowly like putty (same rate fingernails grow). • 250 Km thick 3. Mesosphere • “Middle Sphere” • Strong lower mantle. • High Density Solid rock that flows in circles, heating and cooling. 4. Outer Core • Liquid layer • Made of melted Iron • Very Dense • 2,200 Km thick • How do we know this layer is liquid??? 5. Inner Core • Solid Iron • Most dense layer • 1228 Km thick • Iron causes magnetic fields Structural layers