* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Minerals
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
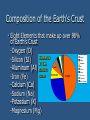
Rocks & Minerals Element Quiz: Give the Symbol 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Oxygen Hydrogen Iron Potassium Silicon 6. Aluminum 7. Calcium 8. Sodium 9. Carbon 10. Magnesium Answers to the Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. O H Fe K Si 6. Al 7. Ca 8. Na 9. C 10. Mg Minerals What is a Mineral? Naturally Occurring Inorganic Solid Definite Chemical Formula Definite Crystal Structure Naturally Occurring Formed by natural processes not in the laboratory. Minerals are inorganic- are not alive Example Salt is a mineral Sugar is not – it was harvested from plants Bling Bling Diamond is a mineral Cubic zirconia is NOT Definite Crystal Structure Highly ordered atomic arrangement of atoms in regular geometric patterns Apatite Feldspar Diamond Quartz 8 Definite Chemical Formula Minerals are expressed by a specific chemical formula -Gold (Au) -Calcite (CaCO3) -Quartz (SiO2) -Pyrite (FeS2) Composition of the Earth’s Crust Eight Elements that make up over 98% of Earth’s Crust -Oxygen (O) -Silicon (SI) -Aluminum (Al) -Iron (Fe) -Calcium (Ca) -Sodium (Na) -Potassium (K) -Magnesium (Mg) Where Do Minerals Come From? Precipitation Crystallization of Magma Pressure and Temperature Hydrothermal Solutions Precipitation Earth water sources contain dissolved substances which can react to form minerals Evaporation Crystallization from Magma As magma cools elements combine to form minerals Magma Temperature and Pressure Form when existing minerals are subject to changes in temperature and pressure Hydrothermal Solutions When very hot water and substances come in contact with one another reactions occur and minerals can form How Are Minerals Identified? Color Luster Hardness Streak Density Crystal Shape Cleavage and Fracture Special Properties Color Usually the first and most easily observed -Some minerals are always the same color -Some minerals can have many colors ROSE QUARTZ QUARTZ SMOKY QUARTZ Luster General appearance of a mineral surface in reflected light Glassy-Obsidian Hardness Resistance to scratching by different items; “scratchability” Mohs Hardness Scale >2 fingernail 3 penny ~5 Steel of a pocket knife 5.5 Window Glass 6.6 Steel of a file 7 quartz crystal Mohs Mineral Hardness Scale 1) Talc Softest 2) Gypsum 3) Calcite 1 5 4) Flourite 5) Apatite 9 2 6) Feldspar 6 7) Quartz 8) Topaz 3 7 9) Corundum 10) Diamond 10 Hardest 4 8 Streak The color of a finely powdered mineral Determined by rubbing the mineral on a piece of unglazed porcelain (streak plate) Density The amount of matter in a given space (Mass/Volume) Crystal Shape Minerals have a characteristic crystal shape resulting from the atomic packing of the atoms when the mineral is forming Cleavage and Fracture Cleavage is the tendency of a mineral to split or crack along parallel or flat planes Fracture occurs when a mineral breaks at random lines instead of at consistent cleavage planes. BIOTITE 1 Direction of Cleavage QUARTZ No Cleavage Obsidian Conchoidal Fracture Special Properties Magnetism (Magnetite) Glowing under ultraviolet light (Fluorite) Salty taste (Halite) Smell (Sulfur) Magnetite Reaction to HCl (Calcite) Economic Importance of Minerals Minerals are in many things we see and use everyday such as; bricks, glass, cement, plaster, iron, gold Every American Requires 40,000 Pounds of New Minerals per Year at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings -3593 lbs aluminum (soda cans, aircraft) -32,700 lbs of iron (kitchen utensils, automobiles, buildings) -28,213 lbs of salt (cooking, detergents) -1,238,101 lbs of stone, sand, gravel, cement (roads, homes, etc.) Minerals Pop Quiz 1 2 3 4 What are two characteristics of a mineral? Define Luster. What is one way minerals form? Why is color not the best way to identify a mineral?