* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1.4 Earthquakes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
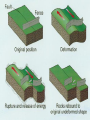
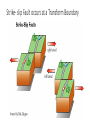
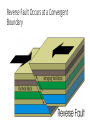
Unit 1.4 Earthquakes Where do earthquakes Occur? • Earthquakes can occur near the Earth’s surface or far below the surface. • Most earthquakes occur at plate boundaries, but some happen at faults located in the middle of tectonic plates. Earthquake Locations Around the World Vocabulary to Know • Stress: Force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume • Fault: When enough stress builds up and rock breaks • Tension: Stress force that pulls on Earth’s crust causing rock to stretch in the middle • Compression: Stress force that squeezes rock until it folds or breaks • Epicenter: The point on the Earth’s Surface above an earthquake’s starting point • Focus: The point inside the Earth where the earthquake begins What Causes Earthquakes? • Earthquakes are caused by movement along faults. • When stress is placed on rocks it deforms, or changes. • This is called Elastic Deformation • Rock is stretched and bent until it can no longer take the stress. • When enough stress builds up in the rock it, it slips and energy is released. • The rock then returns to its original shape. This is called Elastic Rebound. Think of a rubber band, you can only stretch it so far until it breaks and return to its original shape. • This energy is felt as an earthquake. 3 Types of Faults Associated with Earthquakes PLATE MOTION FAULT TYPE Transform : plates move past each other Strike –Slip Fault: Fault Blocks move past each other Convergent: Plates move together Reverse Fault: Fault Blocks move together Divergent: Plates Move Apart Normal Fault: Fault Blocks Move Apart Strike- slip Fault occurs at a Transform Boundary Reverse Fault Occurs at a Convergent Boundary