* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 117 Ways to Pass the Earth Science Regents
Diamond anvil cell wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Milankovitch cycles wikipedia , lookup
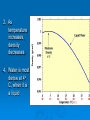
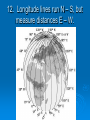
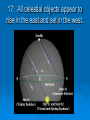
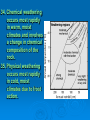
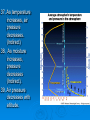
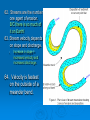
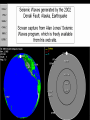
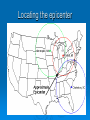
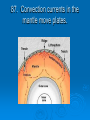
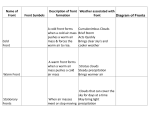
Get Ready to Pass the Earth Science Exam NOTE: THIS PICTURE SHOWS A STUDENT STUDYING – SOMETHING MOST OF YOU HAVE NEVER TRIED. IT WORKS! 1. The same substance always has the same density 2. As pressure increases, density increases 3. As temperature increases, density decreases 4. Water is most dense at 4o C, when it is a liquid 5. Water expands when it freezes 6. Most changes are cyclic 7. The true shape of the Earth is an oblate spheroid, but from space it looks like a perfect sphere. 8. The best model of the earth is a sphere 9. The altitude of Polaris is equal to your latitude on Earth! 10. To determine the earth’s circumference, the altitude of the sun is needed at 2 locations. 11. Latitude lines run east-west, but measure distances N – S. 12. Longitude lines run N – S, but measure distances E – W. 13. Longitude is based on observations of the sun. 14. The closer the isolines (isobars, isotherms, contours), the steeper the gradient! 15. The earth rotates from West to East (24 hours) or counterclockwise 16. The earth revolves counterclockwise around the sun (365 ¼ days) 17. All celestial objects appear to rise in the east and set in the west. 18. The moon has phases because of the angle at which we view it (Half is ALWAYS lit!). 19. Planets appear to go backwards (retrograde motion) as the earth passes them in space. 20. Summer Solstice is June 21st 21. Winter Solstice is December 21st 22. Equinoxes: March 21st and September 21st 23. The equator always receives 12 hours of daylight. 24. The lower the altitude of the sun, the longer the shadow it casts. 25. Foucault’s pendulum and the coriolis effect prove the earth rotates. 26. Earth is closer to the sun in the winter. Winter 27. The closer the planet is to the sun, the faster it moves! 28. Black absorbs/white reflects. Good absorbers are good radiators. 29. The half-life of a radioactive element cannot be changed! 30. Ocean crust is thin and made of basalt. 31. Continental crust is thick and made of granite! 32. Energy moves from source to sink (high concentration to low concentration). 33. Mountains form by uplift. 34. Chemical weathering occurs most rapidly in warm, moist climates and involves a change in chemical composition of the rock. 35. Physical weathering occurs most rapidly in cold, moist climates due to frost action. 36. Air moves clockwise and outward around a high pressure system. 36. Air moves counterclockwise and toward the center of a low pressure system. 37. As temperature increases, air pressure decreases. (Indirect) 38. As moisture increases, pressure decreases (Indirect). 39. Air pressure decreases with altitude. 40. High pressure is cool and dry; low is warm and wet! 41. Winds are due to air pressure differences. 42. Wind blows from areas of high pressure to low pressure 43. Wind is named from the direction it is coming! 44. The closer the air temperature and dew point temperature the greater the chance of precipitation (increased humidity). 45. Weather moves from West to East in the United States. 46. Cold Front 47. Cold fronts move the fastest! Cold fronts force warm air up and are associated with short narrow bands of heavy precipitation and thunder/lightning in advance of the front! 48. Warm Front Warm fronts ride up the back of cold air and produce longer periods of steady rain and occur both in front of and behind the advancing front. 49. Occluded Front 50. Porosity does NOT depend on particle size. 51. As particle size increases, permeability increases! 52. Capillarity increases when particle size decreases. 53. Potential evapotranspiration depends on temperature. 54. Dynamic equilibrium means balance. 55. Apparent diameter of objects (sun, moon) gets larger when the object is closer to Earth (perihelion/perigee) 56. Vertical rays (overhead sun) can occur between 23 ½ o N and 23 1/2o S. 57. Index fossils are good time markers (widely spread, lived a short time). 58. Air cools as it rises. 59. Water bodies moderate temperature (cooler summers/warmer winters) along the coast. 60. Expansional cooling: Orographic effect! 61. Gravity is the primary force behind ALL erosional agents! 62. Streams are the number one agent of erosion. B/C there is so much of it on Earth! 63. Stream velocity depends on slope and discharge. 1. Increase in slope = increased velocity and increased discharge. 64. Velocity is fastest on the outside of a meander bend. 65. Heavy, round and dense particles settle out first (Graded bedding). 66. Bedding (vertical sorting): biggest sentiments are on bottom! Horizontal Sorting – Biggest is located near the shore 67. Glacial sediments are unsorted, unconsolidated, scratched, create U-shaped valleys! 68. Sedimentary rocks – strata – flat layers – most likely to have fossils 69. Igneous rock: cools fast, small crystals; cools slow, big crystals 70. Metamorphic – banding, foliation or distorted structure 71. Mineral properties depend on internal atomic arrangement. - it will determine the hardness, cleavage 72. Silicon + oxygen = tetrahedron 73. Isostasy: earth’s crust in equilibrium 74. Mid-ocean ridge – new earth being created – sea floor spreading. 75. Trenches – earth being destroyed – subduction zone 76. P waves travel faster than S waves. 77. P waves travel through liquid and solids – S waves only travel through solids. 78. Three (3) seismic stations are needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake. Locating the epicenter 80. In undisturbed strata – the bottom layer is the oldest LAW OF SUPERPOSITION 81. Intrusion and faults are younger than the rock they cut across! 82. Unconformity means erosion followed by deposition. 83. Arid landscape: steep slopes with sharp angles. 84. Humid landscape: smooth with rounded slopes. 85. Uranium 235 dates old rocks. 86. Carbon 14 dates recent living objects. 87. Convection currents in the mantle move plates. 88. When a rock is broken into smaller pieces, surface area increases and weathering increases. SUGGESTIONS PAY ATTENTION TO OUR REVIEWS IN CLASS. IF THERE IS AN AREA THAT YOU FEEL WEAK IN, GO TO MY WEB SITE AND READ OVER THE POWERPOINTS. GO TO THE REVIEW SECTION ON MY WEB SITE AND REVIEW THE POWERPOINTS THERE.