* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
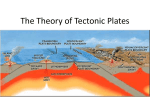
Getting an A in Science • Taking ownership or control of the information learned in class and taking responsibility for your work – This means: • Practicing (reviewing, restating, preparing) • Applying (creating, thinking, using) • Planning (studying, completing projects and homework, being prepared-pencils, books) Continental Drift How many continents are there? 7- North America, South America, Africa, Europe, Asia, Australia, Antarctica Have the continents always looks like this? Were the continents always located in the same position? http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=WaUk94AdXPA &feature=related Puzzle Activity • Cut the continents apart. • Try to assemble the puzzle. • What clues did you use to help you put it back together correctly? A continental puzzle Discovering Earth’s Past • Using your textbook (pages 98-104) complete the worksheet on continental drift and seafloor spreading. • Worksheet is due tomorrow Continental Drift • Who? – Alfred Wegener (German meteorologist) • When? – 1912 • He noticed the puzzle-like fit of the continents http://maps.google.com • He proposed that the continents were joined together in the past, in a large land mass called Pangaea. Describe it • Over time, the continents drifted (moved) apart – Wegener named his theory “Continental Drift”. He supported his theory with four pieces of evidence. 1. Animal Fossil Clues • Matching fossils of animals on once connected land areas. 2. Plant Fossil Clues Fossils of the plant Glossopteris are found in rocks in South Africa, India, Australia, South America, and Antarctica • 3. Climate Clues Glacial evidence in Africa, South America, Australia • Fossils found in Antarctic soil indicate that the now frigid continent was once lush with trees and ferns, and home to dinosaurs, amphibians, and later, marsupials. 4. Rock Clues - similarities and ages Mountains in South America and Antarctica are believed to have formed as part of the same mountain chain. Wegener’s theory made sense, but no one wanted to accept it until they knew HOW the continents moved. Years later someone came up with an explanation of HOW the continents moved Seafloor Spreading • Who? – Harry Hess (A Princeton University scientist) • When? – 1960’s Using new technology, they looked at the ocean floor • Hess and other scientists mapped the ocean floor using sonar • They detected underwater mountain ranges • Further examination of the ocean floor with a submarine showed underwater volcanoes. • A variety of life living near the warm vents of the volcanoes was found • Sampling the rocks near the volcanoes revealed that there was a pattern to their formation. Describe Seafloor Spreading • Magma in the mantle rises and pushes the plates apart, forming new oceanic crust. http://www.absorblearning.com/media/item.action?quick=12n http://education.sdsc.edu/optiputer/flash/seafloorspread.htm Now we could explain HOW the continents moved: Seafloor Spreading causes Continental Drift He supported his theory with two pieces of evidence. 1. Rock ages Youngest rocks are found at the mid-ocean ridges and they become increasingly older farther from the edges. 2. Magnetic Clues • Magnetic iron particles record the time of the rock formation. • When the magnetic north pole switched places, iron in the rocks recorded this information http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BCzCmldiaWQ http://www.absorblearning.com/media/attachment.action?quick=12w&at t=2789 A map of the ocean floor provides even more evidence http://maps.google.com/ Iceland shows seafloor spreading above the water, which makes it easier to study Plate Tectonic Theory • Theory of Plate Tectonics -Earth’s crust is broken into plates which float and move. Earth’s crust made of many plates is similar to the shapes on the outside of a soccer ball. There are about 13 plates covering Earth’s surface Two Types of Plates • Continental Plates – lighter, thicker, made of granite (label your picture) • Oceanic Plates – heavier, thinner, made of basalt (label your picture) Plate Boundaries (edges) • When the plates move, their boundaries, or edges, can scrape each other or collide. • There are three types of boundaries – Convergent – Divergent – Transform Convergent Boundary • Plates move toward each other Convergent Boundary Continental/Continental • What occurs there? – Earthquakes and mountain ranges • Where can we see this? – India into Asia- Himalayas/Mt Everest http://www.absorblearning.c om/media/attachment.action ?quick=12t&att=2783 http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es1105/es1105page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization Convergent Boundary Continental/Oceanic • What occurs there? – Earthquakes , trenches, volcanic mountains • Where can we see this? – Pacific plate is subducting under Japan • Volcanic mountains and deep sea trenches are created along this edge. http://www. absorblearn ing.com/me dia/attachm ent.action? quick=12s &att=2781 Oceanic plate into continental • Example: Pacific plate (oceanic) subducts (sinks) under Japan (continental). http://maps.google.com/ Divergent Boundary • Plates move apart Divergent Continental/Continental • What occurs there? – Earthquakes and rift valleys • Where can we see this? – Africa http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::640::480::/sites/dl/free/0072402466/30425/19_21.swf::Fig.%2019.21% 20-%20Evolution%20of%20a%20Divergent%20Plate%20Boundary Divergent Oceanic/Oceanic • What occurs there? – Earthquakes, mid-ocean ridges (seafloor spreading) and underwater volcanoes • Where can we see this? – Mid Atlantic Ridge https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bGye6vlOpbY Transform Boundary • Plates slide past each other Transform Boundary • What occurs there? – Earthquakes • Where can we see this? – San Andreas Fault, CA https://www.yo utube.com/wat ch?v=4vCsPB ZI2KE San Andreas Fault, CA • Each time the plates slide past each other, an earthquake occurs Review of Plate Motion • There are plates covering the surface of the Earth. • The edges of the plates are called boundaries. • There are three types of motion seen at the plate boundaries. A. Convergent B. Divergent C. Transform 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nazca and South American Plates? Indian and Eurasia Plates? Australian and Antarctic Plates? N. American and Eurasia Plates? N. American and Pacific Plates (near CA?) What causes the plates to move in these different ways? Asthenosphere • A plastic-like layer found below the lithosphere. • The rigid oceanic and continental plates of the lithosphere sit on top The Asthenosphere is heated by the hot Outer Core Convection Current crust mantle core • Hot material rises, cooler material sinks, creating a current, called a Convection Current Convection Currents are like Lava Lamps Hot material rises, cooler material sinks When the asthenosphere moves, it carries the lithospheric plates Convection currents cause plate motion http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=Kpoko_l34ZE http://www.yout ube.com/watch? v=lJiAUvB1vE U http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ryrXAGY1dmE Every time these plates move we get earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and possibly tsunamis