* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TAKS Review
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
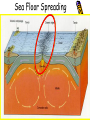
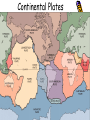
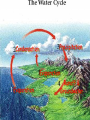
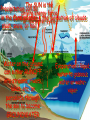
TAKS Review Objective 5 The student will demonstrate an understanding of earth and space systems. Plate Tectonics History • Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift— continents move slowly from Pangaea to present day • Sea Floor Spreading—magma wells up forcing the sea floor apart and forming the mid-ocean ridge • Theory of Plate Tectonics—Earth’s crust is broken into parts called plates that move or float on top of the mantle Continental Drift • Same “fresh water” reptile fossils along South American & African coastlines • Similar rock formations on both the South American & African coastlines • Similar glacier evidence on both continents Sea Floor Spreading Sea Floor Spreading Evidence… Rocks close to the midocean ridge are very young and the age of these rocks continues to increase the farther you get from the ridge Iron bearing minerals show a record of Earth’s magnetic field reversing; these rocks show the same field direction an equal distance on either side of the mid ocean ridge Continental Plates Divergent Plate Convergent Transform Boundary Boundary Boundary Trench-formed where Sea Floor Spreading one plate subducts under another Subduction Zone Plate Tectonics Rift Valley A rift valley is a long, deep valley bounded by normal faults. It forms where the earth’s crust is being pulled apart. A rift valley can appear on land or beneath bodies of water, where two continental plates are separating, or on the ocean floor along the crest of a mid-ocean ridge, where new ocean crust is forming. Rotation Earth rotates or spins on its axis, taking ~24 hrs to make one rotation. This is what gives us day and night. Revolution The revolution of the Earth around the sun takes 365.25 days. This is what brings us the seasons. The Moon • Rotates on its axis once every 29 days • Revolves around the Earth once every 29 days • Therefore, we always see the same side of the moon Moon Phases New Moon = no reflected light • We see the moon because it reflects light from the sun Full Moon = full • phases caused by moon’s circle of reflected revolution around the Earth light • phases are named for the lit portion of the moon •Waxing = getting lighter; Waning = getting darker • Crescent & Gibbous refer to the shape of the light being reflected Condensation Precipitation Evaporation Evaporation Runoff & Groundwater The SUN is the Precipitation can be driving energy force in the form of rain, Condensation = thecycle formation of clouds of the water sleet, snow, Water or hail Water on the ground can either RUNOFF into streams, rivers, lakes, etc. or percolate through the soil to become GROUNDWATER Cycle Evaporation = liquid water to gaseous water or water vapor Renewable vs. Nonrenewable • Renewable resources are replaced naturally in a relatively short period of time (such as plants) • Nonrenewable resources cannot be replaced as they are used (such as iron & fossil fuels) • Inexhaustible resources are renewable resources with an almost limitless supply (such as wind and sunlight) Endangerment of Species • Can result from human activities having negative effects on the environment • Modification of the water, nitrogen, and/or carbon cycles • Not only can these lead to species endangerment, but also extinction For Example… • Deforestation: the destroying and cutting down of forests – Loss of habitat for millions of species results in their extinction – Fewer trees to take in CO2 and trees are burned producing even more CO2 – Annually, there is an approximate net loss (difference between trees cut down and those planted) of 23.2 million acres…that’s like cutting down a little more than an acre of trees for every single person in Texas. (about the size of a football field) For Example… • Modifying the Carbon Cycle by increasing the amount of CO2 in the air from the burning of trees and fossil fuels for electricity and vehicles of transportation – CO2 is a greenhouse gas; by increasing the levels of CO2, it acts as a blanket on the Earth raising the average global temperature – On a global scale C02 makes the biggest contribution to global warming (about 64%). The C02 concentration in the atmosphere is now about 30% higher than 200 years ago. If it continues to increase at the same rate it could nearly double by the year 2035. Burning of oil, coal and natural gas and the clearing and burning of vegetation are the main causes of the increased levels of this gas. For Example… • Modifying the Nitrogen Cycle can result in the formation of nitric acid and ground-level ozone – Human health concerns include effects on breathing and the respiratory system, damage to lung tissue, and premature death. Small particles penetrate deeply into sensitive parts of the lungs and can cause or worsen respiratory disease such as emphysema and bronchitis, and aggravate existing heart disease – Nitrogen pollution can result in acid rain causing the destruction and possibly extinction of native plant species which in turn can lead to the extinction of those animal species that depend on the native plants For Example… • Demands for water both for consumption and irrigation continue to rise faster than the population rate – Use of rivers causes the flow to be reduced downstream and lakes to dry up resulting in a loss of habitat for native species – Pumping out of water from groundwater sources such as aquifers leads to land subsidence destroying habitat – Rising levels of pollution in water result in less consumable water by living organism causing loss of habitat and possible extinction of species – Draining of water-covered lands such as swamp lands also result in habitat destruction and loss of species Reminders… • Plate tectonics is the movement of crustal plates which can lead to sea floor spreading, formation of rift valleys, mountain building, and other landform changes • The moon goes through a cycle of changes both visually (phases) and forces acting on the Earth (tides) • Species endangerment/extinction can be the result of human activities as well as natural events modifying nature’s cycles • Energy from the sun drives our weather as is an almost inexhaustible resource »Any questions???