* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Currents experiment
Underfloor heating wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Cutting fluid wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Reynolds number wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Building insulation materials wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
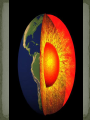
1. Tension is a force that pulls on the plates (lithosphere)…. What does tension look like? 2. Compression is s force the pushes on the plates (lithosphere). What does compression look like? 3. Shearing is a force that pushes on the plates causing one to move in one direction and the other plate to move in opposite direction. What does shearing look like? 4. Where does do the forces come from to cause the lithosphere to move? 1. CW: P.O.C.E.R. & heat transfer HW: Read 1.2 in your text book “Convection and the Mantle” Take Cornell notes Use a small index card to put on top of the beaker of test tube you are going to put on the top. Then once each container is on top of each other then carefully pull out the index card. Hold the containers carefully for several minutes and observe what happens to the solutions. You should be asking yourself what does this have to do with forces and the movement of the lithosphere? Predict What will happen to the two solutions? What will happen to the two solutions? Observe Before Before Explain After After In which layer of the earth would you expect to find the mixing of the two solutions (purple)? Why? CW: Convection Current & heat transfer HW: None What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it becomes hotter? Describe how convection currents form. Name two layers of Earth in which convection currents take place. What causes convection currents in the mantle? In your pod Define radiation….. Next, Define Conduction….. Next, Define convection….. Heat transfer with no contact taking place between the heat source and an object. Heat transfer within a material or an object when direct touching is taking place. Heat transfer by the flow of an energized fluid. This flow usually happens form one part of fluid to another part. In your pod Provide several examples of radiation….. … Next, Provide several examples of conduction ……. Next, Define Provide several examples of convection….. …… What does density have to do with the flow of a fluid / convection current? Hint: Once a flow of energized fluid begins does it lose its energy? What will happen next…. How would you describe atoms as they gain energy? Do these particle become less dense or more dense? How would you describe atoms as they lose energy? Do these particle become less dense or more dense? 1. The core of Earth is really hot. How do you think this affects what happens to the materials within the mantle? 2. How does the mantle and the materials within the mantle affect what happens on the crust & lithosphere? 3. .