* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes - Ms. Inden's Geography 12 Website | When one
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
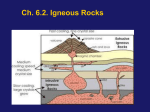
Volcanoes Geography 12 Ms. Inden Volcanology; volcanologist The study of the ways solid, liquid or gaseous materials are forced into the earth's crust or ejected onto the surface; a person who does this studying A few terms • Molten – melted • Magma – molten rock when it is still underground • Lava – magma that has reached the surface http://www1.moe.edu.sg/learn@/Quest/winners/primary/yu_neng_pri_volcano_nc/qpixa.jpg Where does magma come from? • Radioactive decay or uranium and thorium • Friction created by the movement of plates • The magma develops in a magma chamber below the earth http://www.georesources.co.uk/volgen.htm Ka-boom! • The rock expands as the temperature rises, and also gas is produced • This causes pressure underground • The magma will erupt (now lava), along with gasses, steam, ash, volcanic bombs and rock fragments • The eruption, and the violence involved depends on the sort of volcano the type of rock involved (more on this later) Animation of a strata volcano • http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/ animations/volcanoes/index.html Extrusive • When lava or other materials reach the surface they are called extrusive • Form extrusive igneous rock when cooled Intrusive • When magma is injected into the crust (never reaching the surface), it is called intrusive • Form intrusive igneous rock when cooled • Sometimes exposed through erosion You need to know batholith, laccolith, sill and dike Which landforms on this image are intrusive, and which are extrusive? What would cause a batholith to be exposed? http://www.indiana.edu/~geol105/images/gaia_chapter_5/dike&sill.jpg Intrusive landforms • Most magma is intruded • Intrusive igneous rock has bigger crystals than lava which is cooled quickly at the surface • Batholith – at least 100 km, magma cools slowly • Sill – horizontal intrusion • Dikes – cuts through bedding planes vertically • Laccolith – smaller than batholith - fills up a chamber or cavern • This volcanic flow probably ran into a glacier, or possibly a cliff – this part of the lava cooled quicker, creating these columns • Look for columns like this on the highway toward Vancouver – south of Quesnel • Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland http://www.geolsoc.org.uk/webdav/site/GSL/shared/images/geoscientist/GiantsCausewayrersized.jpg