* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
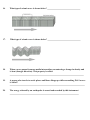
Review Chapter 3 – Earth’s Structure Name: _______________________________ Period: _______ 1. Label Figure 1with A, B, etc..by selecting from the list below. A. B. C. D. E. F. Mantle Mesosphere Core Lithosphere Crust Asthenosphere _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ Figure 1 2. What changes occur with depth into the Earth? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____ 3. What metals are present in the Core? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______ 4. In the outer, liquid layer of the Core circulation of this metal believed to create Earth’s magnetic field (circle the correct answer). A. Iron B. Nickel C. magma D. Silicate 5. The outer Core remains liquid due to the (circle the correct answer). A. temperature B. corn starch C. pressure D. water content 6. The asthenosphere moves because of heat transfer by ___________________________ that sets up currents. 7. Describe the asthenosphere’s physical properties: ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 8. Describe the mesosphere physical properties: ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 9. What metal is abundant in the Crust? ___________________________________ 10. Silicates are abundant in the Crust and are compounds made up of silicon, _______________, and another element. 11. Which layer makes up 82% of the Earth’s volume? (circle the correct answer): A. crust B. mantle C. core D. lithosphere 12. Describe the lithosphere, what layers of the Earth does it contain? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 13. How does Oceanic Crust differ from Continental Crust? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 14. From which layer of the Earth does the “magma” that feeds volcanoes come? (circle the correct answer): A. asthenosphere B. mantle C. core D. lithosphere 15. The study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the earth is called __________________________________. 16. What type of seismic wave is shown below? _________________________________ 17. What type of seismic wave is shown below? _________________________________ 18. When a wave passes from one media into another encountering a change in density and is bent (changes direction). This property is called: __________________________________________________________________________ 19. A person who travels to exotic places and blows things up while researching P & S waves is called? ___________________________________________________________________________ 20. The energy released by an earthquake is sensed and recorded by this instrument _____________________________________________________________________ 21. What is happening to the S waves shown below and what does this tell us about the outer layer of the Earth’s core? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Core 22. The “Moho” is the chemical boundary between which 2 layers of the Earth? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 23. What was the significant outcome of the Molehole Project? ___________________________________________________________________________ 24. A shadow zone that occurs during an eatthquake is a region on the Earth’s surface where (circle the correct answer): A. light is not detected B. only P waves are detected C. only S waves are detected D. no seismic waves are detected.