* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
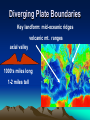
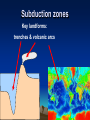
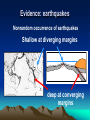
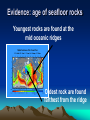
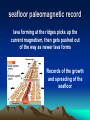
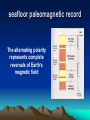
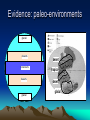
Plate Tectonics Definition Plate: Rigid, rocky outer surface of the Earth Tectonic: To build or destroy The processes by which the rocky plates of the planet move and interact with each other Internal Structure of the Earth lithosphere plates inner core solid iron mantle hot dense rock outer core liquid iron Lithospheric Plates Oceanic: Continental: thin, heavy, mostly lava flows thick, light, mostly granite Asthenosphere Weak, plastic upper mantle Lithospheric Plates Diverging Plate Boundaries Where plates pull apart from each other Stretching & thinning High heat flow (New Crust Created) Diverging Plate Boundaries Key landform: mid-oceanic ridges volcanic mt. ranges axial valley 1000’s miles long 1-2 miles tall Converging Plate Boundaries Where plates collide Subduction zone: collision between oceanic and continental lithosphere (Crust Destroyed) Subduction zones Key landforms: trenches & volcanic arcs Transform Plate Boundaries Where plates slide side by side Key landform: faults (Crust neither destroyed or created) Driving Force thermal convection / convection currents pushes up at ridges plates spread away hot rock cold rock plate sinks and subducts Geologic activity at plate margins Volcanism: C, D Earthquakes: C, D, T Rock Deformation: C, D, T Evidence: shape of continents Africa South America The margins of some continents look like they could fit together First proposed by Alfred Wegner Fossil Evidence Evidence: volcanoes Nonrandom occurrence of volcanic activity Evidence: earthquakes Nonrandom occurrence of earthquakes Shallow at diverging margins x x x x x x x xx x deep at converging margins Evidence: hot spots Stationary upwellings of heat away from plate margins Evidence: hot spots As plates move, the volcanoes are carried away from the hot spot Only volcanoes near the hot spot are are active Can determine direction and speed of the plate motion Evidence: age of seafloor rocks Youngest rocks are found at the mid oceanic ridges Oldest rock are found farthest from the ridge Evidence: paleomagnetism Earth has a strong magnetic field Iron rich volcanic rocks record Earth’s magnetic field at the time they form seafloor paleomagnetic record Bands of alternating polarity Symmetrical about the mid oceanic ridges seafloor paleomagnetic record lava forming at the ridges picks up the current magnetism, then gets pushed out of the way as newer lava forms Records of the growth and spreading of the seafloor seafloor paleomagnetic record The alternating polarity represents complete reversals of Earth’s magnetic field continental paleomagnetic record The location of magnetic poles on separate continents appear to wander with time If the poles haven’t moved significantly, then the continents did Use overlapping poles to reconstruct the past positions of the continents Plate Tectonics in the PNW Mt Meager M t C ay le y Mt G ar ibal di Mt B ak er G la cie r P ea k an u J de Fu ca North American Mt Rai nier Mt St Helen s Mt Adams Mt Hood Mt Jefferson Thr ee S is te r s C ra ter La ke Pacific Mt M c Loughin M t S has ta L as s e n P e ak Sa nd nA 0 r ea 20 0 a sF km Cascadia subduction zone ult Plate Tectonics in the PNW Cascades volcanic arc Cross section of the Cascadia Subduction zone East West 150 miles Coast Range Pacific ocean Willamette valley su bdu cti ng oc ean ic Western Casc ades High Cascades volcanoes Desc hutes basin 60 miles pl ate partial melting Plate Tectonics in the PNW Mt Meager M t C ay le y Mt G ar ibal di Mt B ak er G la cie r P ea k an u J de c Fu a North American Mt Rai nier Mt St Helen s Mt Adams Mt Hood Mt Jefferson Thr ee S is te r s C ra ter La ke Pacific Mt M c Loughin M t S has ta L as s e n P e ak Sa nd nA 0 re a 20 0 a sF km Juan de Fuca & Gorda mid ocean ridges ult Plate Tectonics in the PNW Mt Meager M t C ay le y Mt G ar ibal di Mt B ak er G la cie r P ea k North American Mt Rai nier Ju an de Fu ca Mt St Helen s Mt Adams Mt Hood Mt Jefferson Thr ee S is te r s C ra ter La ke Mt M c Loughin Pacific M t S has ta L as s e n P e ak Sa nd nA 0 re a 20 0 a sF km Blanco & Medocino fracture zones ult Plate Tectonics in the PNW “exotic terranes islands carried by the plates Attached to the North America continent seafloor paleomagnetic record Bands of alternating polarity Symmetrical about the mid oceanic ridges Evidence: paleo-environments glacial deserts desert coral reefs deserts tropics desert glacial glacial Evidence: distribution of mountains Importance of Plate Tectonics