* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
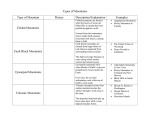
How are mountains formed? Why do mountains form? Types of Mountains Folded Fault Block Dome Volcanic Eroded plataeus Mountains are made in several ways. Let’s take a closer look . . . • Folded Mountains - These are formed as layers of the earth react to forces pushing in on either side, much as a piece of paper folds when pushed together. • Fault Block Mountains - These mountains form when faults or cracks in the earth's crust force some materials or blocks of rock up and others down. • Dome Mountains - These mountains are the result of a great amount of melted rock pushing its way up under the earth. Over thousands of years the dome mountains form in the place where the earth is pushed up. • Volcanic Mountains - These are formed from the vast amounts of lava that have hardened after spurting out of a volcano. • Residual Mountains - These are mountains that are really plateaus that have worn down from erosion. Folded Mountains • Folded mountains are formed when land is in between two plates and those plates are pushing toward each other. When this happens the land begins to fold to form mountains. • Layers of folded rock look like waves. • They have upfolds and downfolds. • An upfold is called an anticline and is a fold that folds towards the sky and the bend is on top. • A downfold is called a syncline and is a fold that folds toward the ground. Folded Mountains Anticline Syncline Appalachians - the site of an ancient continental collision Folded Mountains - the Blue Ridge Fault Block Mountains • When continental plates push together, the layers of rock may also crack and break; and then they become forced up and down along the breaks or faults as they are called by geologists. Cracks or faults Strata originally deposited in horizontal layers become tilted. Erosion occurs over time! Magma rises toward the surface pushing up the land above; later the above layers erode leaving an igneous dome or pluton. Sometimes called plutonic mountains from Pluto, Roman god of the underworld. Mt.Fuji, Japan Three types of volcanic mountain cones are: • Cinder or Tuff Cones - small symmetrical cones formed from cooled lava ejected into the air • Composite or Strato volcanoes - very large and steep near the summit and broad at the base; formed from layers of “thick” viscous lava and layers of ash • Shield volcanoes - very broad and flat and large ; formed from “runny” (very low viscosity) lava that flows easily; they look like a warriors shield lying on the ground from distance Active cinder cones from Iceland-very explosive Note the relatively small size as compared to the other types. These are eroded cinder cones in Idaho. Mayon, Philippines Mt. Fuji, Japan Composite or Strato volcanoes are extremely dangerous and explosive on a large scale. Popocatepetl near Mexico City Mt.. Vesuvius, Pompeii, Italy Mount St.. Helens, Washington Popocatepetl is a snow capped strato volcano that stands 13,776 (4200 m) above the surrounding basin. The name Popocatepetl, meaning “smoking mountain”, was given to the volcano by the Aztecs, and suggests that the volcano has long been active. Popo, as it is often called, is built on an older volcano which adds 12,464 ft (3800 m) to Popocatepetl's elevation. Huge snow and ice covered strato volcanoes - Some of the sleeping giants of the Cascade Range Mt. Ranier Mt. St. Helens Lahars- hot mud slides - how do you think they form? Mauna Loa, Hawaii - world’s largest volcano. Shield volcanoes are characterized by “runny” lava. The lava will run for miles; this causes a broad and flat volcano. These volcanoes are not very explosive. Fountaining produces Aa and ground flows produce pahoehoe! When an area of highand remains standing above the general level after rivers and other natural agents have lowered the surface of the surrounding area, the name residual mountain is used. Sometimes such highands are called 'mountains of denudation'. This term can usually be applied to the mountain ridges associated with 'dissected plateaux'. Included in this class are the mountain ridges of the Highlands of Scotland, the Sierras of Central Spain, and the Mesas and Buttes of the western plateau lands of the United States. •Formed from eroded plateaus. •Buttes, mesas, rock spires are common features. Monuments Nat’l Park The Southwest- USA Goose Canyon Mesa Verde Canyonlands Monuments Nat’l Park Bibliography http://ea.bemidji.msus.edu/truedson/psns/ch22b/tsld004.htm http://volcano.und.edu/ http://www.americansouthwest.net/html http://www-glg.la.asu.edu/~sreynolds/geologic_scenery/ http://www.homestead.com/parkview/Folded.html http://www.pittsford.monroe.edu/Schools/Jefferson/Maps&Glob es/Mountains.html http://www.swparks.com/