* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Nitrogen fixing bacteria De
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
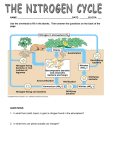
Nutrient Cycles The water cycle, nitrogen cycle and carbon cycle The Water Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen • All organisms need nitrogen to make proteins. • Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of our air but it cannot be used directly by most organisms. • Organisms get nitrogen from substances that contain nitrogen. Examples? De-nitrifying bacteria Nitrogen fixing bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Nitrogen-fixation • Nitrogen-fixing bacteria can convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. • Without these bacteria the nitrogen cycle would stop. • The only other natural nitrogen-fixing process is lightning which accounts for about 1% . Nitrogen-fixing Bacteria • occur in nodules on the roots of legumes such as peas, beans, and alfalfa. These bacteria provide usable nitrogen to the plant. • live freely in soil and water but the ammonia they create cannot be used directly by most plants. • Soya beans • Nodules on roots contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria Photo Credit: Jennifer Dean Lightning naturally fixes nitrogen in the atmosphere and changes it into ammonia. Ammonia in soil • Nitrifying bacteria fixing convert ammonia Nitrogen bacteria to nitrites and then nitrates which plants can absorb through their roots. De-nitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Animals get the nitrogen they need by eating plants or animals. • When nitrogen is digested, ammonia is formed and this toxic product is removed through the animal’s waste and returned to the soil. • Bacteria and fungi in the soil break down the ammonia into nitrites and nitrates where they are released into the soil to be used by plants. Returning Nitrogen to the Air • Denitrifying bacteria in the soil convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas. Nitrogen fixing bacteria Denitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria The Nitrogen Cycle The Carbon Cycle The Carbon Cycle • All living things contain carbon. • Carbon dioxide makes up 0.04% of the gases in the atmosphere. • Carbon dioxide provides all of the carbon that plants need to grow. • Carbon reservoirs include: – all the forests in the world, – the oceans where CO2 is dissolved in the water – and fossil fuel deposits of coal and oil. • Photosynthesis and respiration move carbon between the various reservoirs and provides the method for the flow of energy through an ecosystem. Photosynthesis and Respiration Photosynthesis • Process plants use to capture the sun’s energy and convert it into another form: • Food! • Plants use chlorophyll to capture the sun’s energy. CO2 + water Sunlight energy glucose + O2 Respiration • The O2 produced by the plants provides the O2 we need to live! • The glucose made during photosynthesis is used by the plant to live and grow. • The energy from the glucose is released during cellular respiration. glucose + O2 CO2 + water + energy Photosynthesis vs. Respiration CO2 + H2O + sunlight C6H12O6 + O2 C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy