* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryotes
Survey
Document related concepts
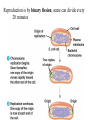
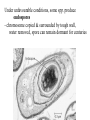
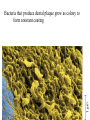
Transcript
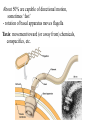
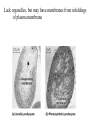
This week in lab: sampled trees in 2 habitats at Green Oaks, ‘Old Growth’ & Spoil Banks - your assignment: 1) Use the supplied data & your lab handout to calculate Shannon-Weiner Diversity Indices & Schoener’s Community Similarity Index 2) Answer the questions on assignment sheet (back of room, or on the course website) Last day… we were discussing the major changes occurring during the history of life, including mass extinctions Included the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-T) extinction event that wiped out dinosaurs and much more Luis and Walter Alvarez The K-T extinction was not the worst ever… - late in Permian, massive volcanic eruptions causing lava flows, ash, and cooling of climate - extensive glaciation - turn-over of ocean waters brings oxygen depleted water, CO2 and hydrogen sulfide to surface Extinction of most living species (>90% of marine spp.), and end of Paleozoic era. History of life characterized by great changes in flora and fauna due to extinction & evolution - response to mobile continents & constantly changing climate Fossil record incomplete, but does document many sweeping changes in living things *Required* reading: Chapt. 25, pp. 507-524 This long history of life has resulted in an enormous diversity of organisms on the planet - we will try to survey some of this diversity... Traditionally, organisms classified as plants or animals (Kingdoms Plantae & Animalia) - but many species do not fit readily into these categories... - a five kingdom system became popular after 1969 - but still does not reflect relationships well, or do justice to diversity of smaller organisms... A three domain system is a starting point for organizing all of these species: Bacteria, Archaea, & Eukarya The first two domains are traditionally grouped as ‘prokaryotes’: - simpler internal structure than eukaryotic cells (no nucleus or other membrane enclosed organelles such as mitochondria) Generally tiny (1-5 m), though some only... tiny Found almost everywhere... - soil, water, in & on other organisms - places too hot or cold or inhospitable for most life - usually do require moisture Most ‘prokaryotes’ are unicellular, a few may be colonial - come in various shapes, especially cocci, bacilli, and spiral forms Normally have a cell wall - protects, maintains shape & prevents bursting in hypotonic conditions Cell walls contain peptidoglycan (sugars linked by peptides) - thick outer layer in gram positive bacteria, thinner layer between membranes in gram negative Some are covered with sticky capsule (polysaccharide or protein) - helps stick to surfaces, protects Some use fimbriae (short, hairlike) to stick to each other or surface May also use pilus (pl. pili) to hold on, or to exchange DNA - horizontal gene transfer About 50% are capable of directional motion, sometimes ‘fast’ - rotation of basal apparatus moves flagella Taxis: movement toward (or away from) chemicals, conspecifics, etc. Lack organelles, but may have membranes from infoldings of plasma membrane ‘Prokaryotes’ have single, circular ‘chromosome’ - few associated proteins May also have smaller DNA rings called plasmids that often carry ‘specialized’ genes (e.g. antibiotic resistance) Reproduction is by binary fission, some can divide every 20 minutes Under unfavourable conditions, some spp. produce endospores - chromosome copied & surrounded by tough wall, water removed, spore can remain dormant for centuries ‘Prokaryotes’ exploit a wider range of resources than all eukaryotes combined ‘Prokaryotes’ may be obligate aerobes (require O2 for aerobic respiration), facultative anaerobes (use O2 when available, or fermentation if not) or obligate anaerobes (must use fermentation or anaerobic respiration) All organisms require nitrogen to make proteins, etc., but only certain prokaryotes can fix N2 to produce ammonia NH3 (nitrogen fixation) Some ‘prokaryotes’ form colonies, and may show cooperation or specialization - some cyanobacteria have specialized cells for photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation Bacteria that produce dental plaque grow as colony to form resistant coating Discussing ‘prokaryotes’ as if one uniform group, but far from true... - paraphyletic grouping, Archaea closer to eukaryotes than bacteria Bacteria & Archaea share some ancestral traits Archaea & Eukarya share some derived traits Each domain may also show some unique traits Each group also shows great diversity within... Archaea seem to be less abundant, and often found in extreme environments where other organisms cannot live (e.g. thermophiles, halophiles, methanogens), but new types still being found