* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pathogenic Cocci
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
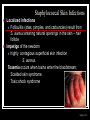
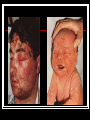
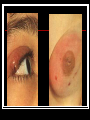
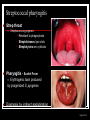
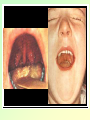
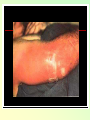
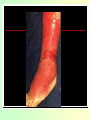
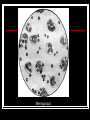
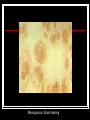
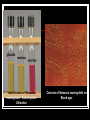
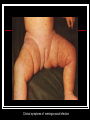
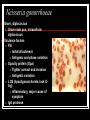
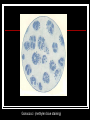
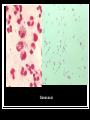
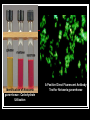
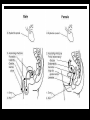
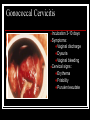
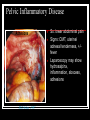
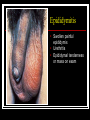
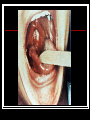
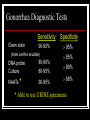
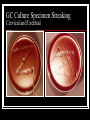
They role in human pathology. Principles of microbiological diagnosis, specific therapy. Lector Tvorko M. S. Classification. S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus VIRULENCE FACTORS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS Staphylococcus epidermidis Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus Growing on Blood Agar Coagulase Test on Staphylococcus aureus Coagulase Test on Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Yelk-salt Agar Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Mannitol Salt Agar. Staphylococcus epidermidis Growing on Mannitol Salt Agar Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar Staphylococcus epidermidis Growing on DNase Agar Staphylococcal Skin Infections Localized infections Folliculitis (sties, pimples, and carbuncles) result from S. aureus entering natural openings in the skin – hair follicle Impetigo of the newborn highly contagious superficial skin infection caused by S. aureus. Toxemia occurs when toxins enter the bloodstream; • Scalded skin syndrome • Toxic shock syndrome Figure 21.4 Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Figure 25.6 Electron Micrograph of Streptococcus pyogenes Note gram-positive (purple) cocci in chains (arrows). Streptococcus are gram-positive cocci classified according to their hemolytic enzymes and cell wall antigens. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (including Streptococcus pyogenes) are the pathogens most important to humans. Produce a number of virulence factors: M protein, erythrogenic toxin, deoxyribonuclease, streptokinases, hyaluronidase. Figure 21.5 Streptococcus in chains (Gram stain) hemolysis reaction - sheep blood agar (alpha) partial hemolysis green color (beta) complete clearing A and B (gamma) no lysis White colonies Beta Hemolysis on Blood Agar (Indirect Lighting) Alpha Hemolysis on Blood Agar (Indirect Lighting) A Plate of Blood Agar showing Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Hemolysis (Indirect Lighting) Gamma Reaction on Blood Agar Streptococcal pharyngitis Strep throat Streptococcus pyogenes Resistant to phagocytosis Streptokinases lyse clots Streptolysins are cytotoxic Pharyngitis - Scarlet Fever Erythrogenic toxin produced by lysogenized S. pyogenes Diagnosis by indirect agglutination Figure 24.3 Streptococcal Skin Infections Erysipelas infects the dermal layer reddish patches Can progress to local tissue destruction Enter the bloodstream Impetigo isolated pustules Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome Cellulitis, myositis and necrotizing fasciitis Figure 21.6, 7 Bacterial Infections of the Heart The inner layer of the heart is the endocardium. Inflammation of the endocardium Endocarditis Subacute bacterial endocarditis – from microbs in the mouth.( Arises from a focus of infection, such as a tooth extraction). alpha-hemolytic streptococci staphylococci enterococci Preexisting heart abnormalities are predisposing factors. Signs include fever, anemia, and heart murmur. Acute bacterial endocarditis Staphylococcus aureus The bacteria cause rapid destruction of heart valves Rheumatic Fever Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune complication of streptococcal infections. Rheumatic fever is expressed as arthritis or inflammation of the heart. It can result in permanent heart damage. Rheumatic fever can follow a streptococcal infection, such as streptococcal sore throat. Streptococci might not be present at the time of rheumatic fever. Prompt treatment of streptococcal infections can reduce the incidence of rheumatic fever. Penicillin is administered as a preventive measure against subsequent streptococcal infections. Antibodies against group A beta-hemolytic streptococci react with streptococcal antigens deposited in joints or heart valves or cross-react with the heart muscle. Figure 23.5 Dental Caries Streptococcus mutans, found in the mouth uses sucrose form dextran from glucose lactic acid from fructose. Bacteria adhere to teeth and produce sticky dextran, forming dental plaque. Acid produced during carbohydrate fermentation destroys tooth enamel at the site of the plaque. Gram-positive rods and filamentous bacteria can penetrate into dentin and pulp. Caries are prevented by restricting the ingestion of sucrose and by the physical removal of plaque. Figure 25.4 Pneumomoccal Pneumonia Streptococcus pneumoniae: Gram-positive encapsulated diplococci Diagnosis by culturing bacteria Penicillin is drug of choice Figure 24.13 Scanning Electron Micrograph of Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pneumoniae (diplococcus). Fluorescent stain Streptococcus pneumoniae on Blood Agar (Indirect Lighting) Enterococcus faecalis in a Blood Culture A bile esculin slant before inoculation. Enterococcus faecalis growing on a bile esculin slant. Note black color. Meningococci Meningococci Gram staining Identification of Neisseria meningitidis : Carbohydrate Utilization Colonies of Neisseria meningitidis on Blood agar Clinical symptoms of meningococcal infection Clinical symptoms of meningococcal infection Clinical symptoms of meningococcal infection Pathological changes of brain (meningococcal infection) Spinal fluid Diagnosis and Treatment of the Most Common Types of Bacterial Meningitis Diagnosis is based on Gram stain and serological tests of the bacteria in CSF. Cultures are usually made on blood agar and incubated in an atmosphere containing reduced oxygen levels. Cephalosporins may be administered before identification of the pathogen. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Gram-, diplococcus Gram stain pus, intracellular diplococcus Virulence factors Pili Initial attachment Antigenic and phase variation Opacity protein (Opa) Tighter contact and invasion Antigenic variation LOS (lipooligosaccharide, lack OAg) Inflammatory, major cause of symptom IgA protease Affected Populations STI Rates World-Wide http://www.agi-usa.org/pubs/ib_std.html Gonococci (methylen blue staining) Gonococci Electron Micrograph of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Colonies of gonococci onto blood agar Identification of Neisseria : MTM Chocolate Agar with a Taxo (Oxidase) Disc Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae : Carbohydrate Utilization A Positive Direct Fluorescent Antibody Test for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae (3) Pili: facilitate attachment, impede phagocytosis Lipopolysaccharide: marked endotoxin activity; local cytopathic effect IgA protease: cleaves IgA-1 subclass of immunoglobulins Neisseria gonorrhoeae (4) Porin (“Por”, formerly protein I): may facilitate endocytosis Opacity proteins (“Opa,” formerly protein II): contribute to attachment to human cells Reduction-modifiable protein (“Rmp,” formerly protein III: stimulates blocking antibodies that reduce serum bactericidal activity GC Sexual Transmission Efficiently transmitted by sexual contact Greater efficiency of transmission from male to female Male to female: 50 - 90% Female to male: 20 - 80% Vaginal & anal intercourse more efficient than oral Can be acquired from asymptomatic partner Increases transmission and susceptibility to HIV 2-5 fold Gonorrhea Many asymptomatic Reason for spread Male- Urethritis, urethral discharge Female - Endocervicitis, discharge, dysuria, bleeding Pharyngitis Proctitis Disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) Pustular skin lesions Septic arthritis Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Endometritis, salpingitis, peritinitis Infertility, ectopic pregnancy Ophthalmia neonatorum Gonococcal Infections in Women Cervicitis Pharyngitis Urethritis DGI Proctitis Accessory gland infection (Skene, Bartholin) Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Peri-hepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis) Pregnancy morbidity Conjunctivitis Many infections asymptomatic Gonococcal Cervicitis Incubation 3-10 days Symptoms: Vaginal discharge Dysuria Vaginal bleeding Cervical signs : Erythema Friability Purulent exudate Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Adhesions Tube STD Atlas, 1997 Sx: lower abdominal pain Signs: CMT, uterine/ adnexal tenderness, +/fever Laparoscopy may show hydrosalpinx, inflammation, abscess, adhesions Gonococcal Infections in Men Pharyngitis Urethritis DGI Epididymitis Urethral stricture Proctitis Penile edema Conjunctivitis Abscess of Cowper’s/Tyson’s glands Seminal vesiculitis Prostatitis Many infections asymptomatic Gonococcal Urethritis Incubation 2-7 days Abrupt onset of severe dysuria Purulent urethral discharge Most urethral infections symptomatic Epididymitis Epididymitis Swollen painful epididymis Urethritis Epididymal tenderness or mass on exam Gonococcal Infections in Women & Men Urethritis Proctitis Pharyngeal infections Conjunctivitis Disseminated Gonococcal Infection Blenorrhea Gonorrhea Diagnosis Intracellular Gram negative diplococci in discharge Growth on selective media, oxidase positive colonies Flourescent antibody Treatment Cover for probable association with C. trachomatis GC Diagnostic Methods Gram stain smear Culture Antigen Detection Tests: EIA & DFA Nucleic Acid Detection Tests Probe Hybridization Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) Hybrid Capture Gonorrhea Diagnostic Tests Sensitivity Gram stain 90-95% (male urethra exudate) DNA probe Culture NAATs * 85-90% 80-95% 90-95% Specificity 95% 95% 99% 98% * Able to use URINE specimens Gram Stain for GC: Urethral Smear Numerous PMNs Gram negative intracellular diplococci Gram Stain for GC: Cervical Smear PMN with Gram negative intracellular diplococci GC Culture Requires selective media with antibiotics to inhibit competing bacteria (Modified Thayer Martin Media, NYC Medium) Sensitive to oxygen and cold temperature Requires prompt placement in high-CO2 environment (candle jar, bag and pill, CO2 incubator) In cases of suspected sexual abuse, culture is the only test accepted for legal purposes GC Culture Candle Jar GC Culture Specimen Streaking Cervical and Urethral GC Culture After 24 Hours Treatment http://www.cdc.gov/STD/treatment/4-2002TG.htm#Gonococcal Prevention Abstinence Safe/”smart” sex Barrier contraceptives Educational programs Reduce misuse of antimicrobials