* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (1526 bp) synthesized on template bacterial DNA of AIDS patients
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
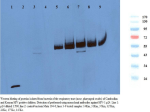
The role of human microbiome in AIDS process Zajac V., Ciernikova S., Wachsmannova L., Adamcikova Z., Stevurkova V., Krcmery V. Cancer Research Institute, SAS, Bratislava, Slovakia Saint Elizabeth University of Health, Bratislava, Slovakia Introduction Despite great success in the diagnostics and therapy of AIDS, there are many unanswered questions. Without giving the answers to these questions more successful treatment of patients can not be expected. The strong argument for this prediction is a fact that it is not possible to stop the worldwide pervation of AIDS, especially in Africa and Asia. The data leading to the conclusion that HIV alone is the etiologic agent responsible for AIDS is generally accepted. According to this claim, virus was transferred to humans from monkeys in Africa through random contacts 35 to 50 years ago, which was not sufficiently confirmed. Plasma HIV RNA is dramatically reduced in patients treated with HAART, but residual viral replication is detected after suppression of plasma viremia. It has also been proven that various forms of HIV reservoirs persist in practically all patients receiving this therapy. Reservoirs were detected in macrophages and other cells of the blood system. • The range of viral reservoirs in the human body is probably very much wider, as is claimed in recent studies. The source of persistent HIV in infected persons remains however unclear. GIT, bacteria and AIDS • There is increase of evidence, pointing out that in the GIT and other mucosal tissue, and not in the blood, is the main place of HIV infection and CD4+T cells loss. These findings go along with new studies on the role of bacterial translocation in the gut as central driver of AIDS pathogenesis. • This interest in investigating bacteria and mycoplasma in this disease was also supported by Montagnier’s finding, confirmed by Shyh-Ching Lo, that mycoplasma is a very important “co-factor” which accelerates the progression of HIV infection in AIDS patients • Bacteria and yeasts represent second kingdom in our body. The fact that the balance between two kingdom is the basis of our existence is still underestimate. • This balance, established for many centuries, was during the last decades seriously disrupped by application of ATBs, pharmaceuticals, drugs and changes in life style (anal sex). • There are new studies on the role of bacteria to antibiotics in diseases associated with AIDS. It demonstrates clearly that bacteria can induce in the gut and the vagina transcription of silenced genes, including HIV-1 provirus. • The HIV-1 has been also detected in the bowel crypt cells and lamina propria. Since these cells are in close nearness to intestinal bacteria, the idea that bacteria can also be involved in the pathogenesis of AIDS is justified. Bacteria are a strong candidate for a viral reservoir in the human body. • These findings are challenging for us to fight against AIDS in a more complex manner. • It is highly desirable to overcome all dogmas and taboos surrounding the disease. In advance, it is necessary to deliberate another potential factors, not only HIV, which may take a part in this disease. Our approach • We study the role of bacteria and yeasts in bovine leukemia and concequently in AIDS process for more than 25 years. • This approach is based on detection of BLV-like sequences in bacteria of BLV positive animals. • Gradually been identified HIV-like sequences in laboratory of prof. F. Wong Staal, UCSD and later HIV-like proteins in bacteria and yeast in a cohort of 80 HIV positive patients from Slovakia, USA, Kenya and Cambodia. Methods used for detection of HIV-like sequences and HIV-like proteins: - Colony and dot-blot DNA hybridization - PCR - sequencing - Western blotting - GPA (gentamicin protection assay) Dot blot hybridization of lymphocyte's and bacterial DNA of AIDS patients. Probe: PCR products 38;39 and 68;69 synthesized on the template of patient's lymphocyte DNA PCR products (1526 bp) synthesized on template bacterial DNA of AIDS patients 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Lines 1-12: M1, P3, P6, P9, P15, Mok1, M11, M12, M15, M21, Mok22. Negative controls in lines 13. PCR without DNA (line 14). Control pBH10 in line15. Used primers: O1,O2 (HIV-1 env gene). Sequences of 348 bp PCR product syntesised on the template of bacterial DNA isolated from AIDS pacient P3, limited by primers O1,O2 (5837-7297) of env gene HIV-1. Identity for 95% with HIV-1 isolate HXB2. Western blotting of proteins isolated from bacteria and yeasts of the respiratory tract (nose, pharyngeal swabs) of Cambodian (Km) and Kenyan (Ke) HIV positive children. Used monoclonal antibodies against HIV-1 gp120 (1:750). lines 1-6 tested samples: 14Km, 17’Ke, 21Ke, 32’Km, 3’Km, 31Km, 14’Ke line 7: serum of AIDS patient diluted 1:100; line 8: control bacteria; line 9: negative control bacteria Muta 104-0. Internalization of HL-60 cells by bacteria of AIDS patients and patients with colorectal tumors (GPA) Patient/clone P15/7 P1/4 P3/3 Mok12/5 Mok 1/6 K1-1 Number of bacterial colonies 2264 1340 1680 lysis of HL-60 cells 181 lysis of HL-60 cells TuSG 71 883 S 104 negat. control <5 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Number of HL-60 cells 2x106/ml Number of bact. cells 0,8x108 Internalization of normal human lymphocytes by bacteria of AIDS patients (GPA) Patient/clone Number of bacterial colonies P15/7 1121 P1/4 complete lyses of human lymphocytes P3/3 complete lyses of human lymphocytes Mok12/5 complete lysis of human lymphocytes Mok 1/6 complete lysis of human lymphocytes K1-1 complete lysis of human lymphocytes Mok 22/5 423 725/5 1140 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Number of lymphocytes 2x106/ml Number of bact. cells 0,8x108 Probiotic treatment of 20 patients (Nissle 1917) Viral load in time of probiotics treatment start: 808 600 Viral load in term of the end of probiotic treatment: 452 190 Decrease of viral load after probiotic treatment: Viral load of 11 patients from 20 decreased (60%) 356 410 (44%) The origin of HIV According to our and other results there is strong objection again generally accepted dogma that HIV was transmitted to humans from apes in Africa about 35-50 or according to last assertion about 100 years ago en route of accidental contacts. That is a good news for Africa. There is not evidence about transmission of retroviruses between two different species in nature. Should be HIV only one exception in nature? Are there adequate proofs for this claim? The problem is that the acceptance of this dubious argument has a major influence on – research, diagnosis and therapy of AIDS. How is it possible that this unconvincing statement was accepted by most experts??? Our hypothesis HIV is an integral part of humans since the beginning of our existance. We inherited it from our ancestors. Bacteria and yeasts are most likely natural host of HIV sequences. • But, there is serious objection – if HIV was in our body from our beginning, why did it’s emerge just about 25-35 years ago? To answer this question we should go back into the ancient history of humankind. In the past, major epidemics frequently occurred when there were new patterns of transport between separately populated areas and new pattern of settlement. This tremendous longtime „sanitary“ process take place mainly in Europe, consequently in USA, GB colonies, partially in Asia and north Africa resulted in establishment of the balance between these two kingdoms in the human population. • This balance was interrupted – intestinal dysbiosis - in the middle of the 20. century due to acceptation of ATBs, drugs (including recreational), medicines and changes in life style (anal sex). Propagated HIV bearing pathogenic microbes in the majority of antibiotics resistance, with the ability to pentrate into the body. When bacteria carrying the HIV sequences with high affinity to lymphocytes penetrated into the blood, infected or lyse them, consequently the immune system has collapsed. The result of this process is ..... AIDS This hypothesis is based on: - respecting the central role of HIV genetic information in the process of AIDS - claims that bacteria and yeasts are most likely natural host of HIV genetic information - recommendation that in AIDS it is necessary to deliberate another potential factors, not only HIV, which may take a part in this disease and may be different in various groups - assumption that transmission of HIV from apes to humans during last decades in Africa as a consequence of their accidental contacts - is not a cause of AIDS. Bubonic plaque epidemic in 1346 very probably induced high frequency CCR5 mutation in the European population. Confirmation of our hypothesis may opens new opportunities for research and treatment of AIDS. Only through open discussion and respect for different views may lead to the elimination of this disease. and now, we are able to answer on many until now unanswered questions Presented hypothesis answer to many until now unanswered questions: - origin of HIV - large scale HIV positivity in Africa - connection of AIDS with TBC in Africa - absence of „gold standard“ in Africa - specificity of AIDS in USA - the presence of HIV reservoirs after antiretroviral therapy - atypical course of disease in comparision with other retroviral infections - the rarity of complete viral particles detection in AIDS patients, but detection of HIV sequences and the HIV-like proteins herein - toxicity of some anti-HIV drugs – AZT and other Dot-blot hybridization of bacterial DNA (0.25 μg) from Cambodian HIV positive children. The hybridization probe was mixture of PCR products that represented gag, pol and env HIV-1 genes synthesized on the template of plasmid pHB10. Samples of 39 patients were applied in lines from A to G. The samples of 8 healthy persons are in lines H and I. In the last line J in position 6 is DNA of tested child with shining clinically expression of disease and in positions 2, 3 are mixtures of aforementioned PCR