* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
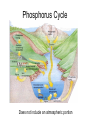
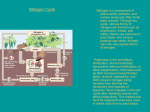
Cycles in Nature Essential nutrients are cycled Biogeochemical cycles through _______________ Biogeochemical • ______________ _________ is the cycle exchange of matter through the biosphere involving living organisms (bio), geological processes (geo), and chemical processes (chemical) Water cycle • Also known as the Hydrologic ____________ cycle • Circular pathway of water ________ on Earth from the atmosphere, to the surface, below ground, and back Water cycle Precipitation • _____________ such as snow or rain falls to Earth • Some seeps into ground, some drops into ponds, puddles and some forms _______ • Some reenters the atmosphere _____________ through evaporation and transpiration Oxygen Cycle • Plants release _________ as a waste oxygen product during photosynthesis ___________ • Humans and other organisms take in oxygen ________ and release _______ carbon ________ dioxide respiration through ____________ Carbon Cycle • Sources of carbon carbon includes: ________ dioxide gas in ________ atmosphere, bicarbonate dissolved ____________ in water, ________ Fossil fuels _______ which are underground deposits of natural gas, oil, or coal, carbonate ___________ rocks, and __________ dead organic matter Transfer of Carbon sun to convert • Plants use energy from ______ carbon dioxide from air into organic material that becomes part of the plant’s structure carbon moves through biotic world as one – _________ organism eats another Carbon Returns to Atmosphere • • • • respiration decomposition Through __________ and ___________ Burning of __________ Fossil ________ fuels Emissions from _________ factories and _______ automobiles methane emitted from wetlands, livestock, _______ and landfills Nitrogen Cycle • 78 % of Earth’s atmosphere is made up of ________ nitrogen gas • However most organisms can only use nitrogen in the form of ions such as ammonium ____________ or _________ nitrate Much of the Nitrogen Cycle occurs underground • Certain types of bacteria can convert nitrogen gas into ammonia through Nitrogen __________ fixation _________ • Acidity in the soil converts the ammonia into ___________ ammonium • Other types of bacteria can convert ammonium into nitrate though ____________ nitrification • Nitrate released by soil bacteria are taken up by ________ which plants convert them into amino acids and proteins continues • Nitrogen _________ along the cycle as animals eat plant or animal matter • When ___________ decomposers break down animal excretions or dead animal and plant matter, nitrogen is returned to the soil as ammonium Lightning breaks • Lightning’s energy _______ apart nitrogen molecules in the atmosphere oxygen • Nitrogen recombines with ________ forming nitrogen oxide • Nitrogen oxide and rainwater forms soil nitrates which are absorbed by ________ Phosphorus Cycle Does not include an atmospheric portion Phosphorus Cycle • Phosphorus is __________ by weathering released of rocks Plants Fungus • _________ and ________ take up phosphate • Moves through cycle as organisms feed on these plants and fungus • ________ and _________ Mining Agricultural runoff increase amount of phosphorus in the environment Summary • The chemical elements, such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, that make up the molecules of living things pass through food webs and are combined and recombined in different ways. • At each link in a food web, some energy is stored in newly made structures but much is dissipated into the environment as heat.