* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Siegel Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
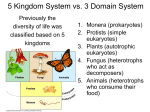
Protists Bacteria Viruses Protists First Single-Celled Eukaryotes Protists means “first” Protists are eukaryotes that are NOT members of the plant, animal, or fungi kingdoms. Why? Uni or Multi? That is the question….. Most protists are unicellular. Some are multicellular. The largest protist is KELP - a brown algae. An Evolutionary Tale Genetic & fossil evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes and are more closely related to present-day Archaea than Bacteria. It is from multi-cellular protist that plants, animals & fungi are thought to arose. Endosymbosis Proposed by Lynn Margulis in 1966 Ancestors of eukaryotes lived in association with prokaryotes. Prokaryotes entered a host cell as undigested food. They eventually began to supply energy to the cell and became an organelle called the mitochondria. Grouping of Protists Protists are often grouped by their mode of nutrition (a.k.a what they eat). Protozoans - animal-like protists that are heterotrophs Plant-like protists - autotrophs, include algae Fungus-like protists - decomposers Animal - like Protists Plant-like Protists Volvox Diatoms Spirogyra Fungus-like Protists How do Protists move? Amoeboid Movement - moving by changing shape: process uses pseudopods Cilia & Flagella - structures supported by microtubules that protrube from the cell surface Passive Movement - non-motile, depend on other means of transportation (I.e. water , water currents) Pseudopod Greek word for “false foot” The cytoplasm of the amoeba streams into the pseudopod and the rest of the cell follows. Amoebas also use pseudopods to surround and ingest prey. Cilia & Flagella Cilia: Short & numerous and they move like oars of a rowboat; protists that move using cilia are known as ciliates. Flagella: relatively long, usually only one or two per cell & they move like a wave from basic to tip; protists that move using flagella are called flagellates. Euglena can use chloroplasts to undergo photosynthesis if light is available or live as a heterotroph by absorbing nutrients from the environment. Passive Movement These protists form spores that can enter the cells of other organisms and live as parasites. Most protists inhabit the body fluids, tissues, or cells of their hosts. Some parasitic protists are important pathogens of animals, including those that cause potentially fatal diseases in humans. For example, Typanosoma causes African sleeping sickness. Malaria is also cause by a parasitic protist. Protists are found almost anywhere there is water. This includes oceans, ponds, and lakes but also damp soil, leaf litter and other moist terrestrial habitats. In aquatic habitats, protists may be bottomdwellers attached to rocks or creeping through sand and silt. Phytoplankton (including algae and prokaryotic bacteria) are the bases of most marine and freshwater food chains. Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic unicellular organisms. What does prokaryotic mean? No nucleus! What kingdom are bacteria in? Monera What Domain are bacteria in? Archaea and Eubacteria Archaea • Single-celled prokaryotes - NOT BACTERIA but sort of like a cousin • Tough outer cell walls that have different amino acids which means that antibiotics may have no effect on these • Most live in extreme environments (extremophiles) 1.Such as undersea hydrothermal vents 2.Great Salt Lake Did you know…. That your intestinal gas (a.k.a farts) are caused by archaea - now there is something to share with your parents at the dinner table tonight! Eubacteria Domain of Germs This domain is responsible for the five second rule and why you don’t eat potato salad left in the sun all day. Have been known and studies for over 150 years All known bacterial pathogens are Eubacteria Discover of Bacteria Bacteria were unknown to people until the 1600s, when Anton van Leeuwenhoek first observed them in his newly made microscope So how do Bacteria fit into our timeline of life? They have the distinction of being the oldest known fossils, more than 3.5 billion years old, in fact! As photosynthesis in cyanobacteria depleted CO2 in the water, layers of calcium carbonate formed STROMATOLITES seen above. Probably most important.. They shaped the course of evolution and ecological change throughout earth's history because they are aquatic (that is they live in water) and are photosynthetic (they can manufacture their own food and produce what along the way?) The genetic material of bacteria is one double-stranded, circular DNA molecule (not surrounded by a nuclear membrane). Classification Rod shape is called Bacillus. Spiral shape is called Spirillium. Spherical is called Coccus. Classify this…. Other important contributions… Many ancient oil deposits are attributed to the activity of cyanobacteria. They are also important providers of nitrogen fertilizer in the cultivation of rice and beans. Other fun bacteria information Where are Bacteria Found? Bacteria are found almost everywhere on Earth: including in the seas and lakes on all continents (including Antarctica), in the soil, and in tissues of plants and animals Food!!!! Bacteria have a wide range of diets. Some are heterotrophs. What are heterotrophs? They eat other organisms. Others are autotrophs. What are autotrophs? They make their own food. Why do you care? Negative effects: a. illnesses (including dental caries, strep throat, cholera, and tuberculosis) Positive effects: a. release nitrogen to plants b. decompose organic material c. fermentation (used in manufacture of cheese and yogurt.) Viruses: Are They Alive? § Life-like in that they have genes and a highly organized structure § However, they are not made of cells nor are they able to reproduce on their own (parasite). § Essentially they are “genes in a box” with a protein coat. Examples Damage by a Virus Depends how quickly the immune system responds to fight the infection Ability of the infected tissue to repair itself For example, recovery from a cold is common b/c our respiratory tissue replaces damaged cells by cell division (mitosis). Damage - continued However, nerve cells don’t divide so damage done by polio is permanent. So prevention of virus diseases like polio is accomplished with vaccines. First vaccine was developed by Edward Jenner for smallpox in the late 1700’s. Vaccines are harmless variations of the virus stimulate the immune system to mount defenses before you get infected Smallpox Contagious No specific treatment Variola major & minor Last case in the US - 1949; last case in the world - 1977 (Somalia) Emerging Viruses Viruses that have suddenly appeared or have recently come to the attention of scientists. E.g. HIV/AIDS, Ebola, Avian flu, West Nile Virus, SARS - just to name a few Where do they come from? Mutations Contact between species which gives way to species jumping through contact and mutations Spread from isolated species Pandemics World-wide outbreaks of a disease Spanish flu (18-month period - 1918 to 1919) killed 20 MILLION ppl worldwide - that is about the same number as the number of ppl who have died in 25 years of fighting AIDS. Bacteriophages Called phages for short - what do you think they infect? Their reproductive cycle is called THE LYTIC CYCLE. An analogy of The Lytic Cycle Alternative to Lytic Cycle Lysogenic Cycle Viral DNA reproduces w/o phage production or death of the cell.