* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
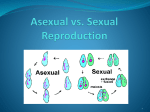
Types of Reproduction Reproductive System Basics Two Types of Reproduction Asexual: A single parent produces offspring genetically identical to itself. BACTERIA Identical Offspring Single-celled organisms. Original parent More uniform offspring Requires one parent REGENERATION occurs when part of an organism grows to form other organisms that are often still connected to the original organism. FRAGMENTATION occurs when the body of the parent breaks into distinct pieces, each of which can produce an offspring. Planaria reproduce by fragmentation and regeneration Starfish reproduce by fragmentation and regeneration BUDDING occurs when a small part of the parent's body separates from the rest and develops into a new individual, eventually becoming an independent organism. Yeast – a type of bacteria that you use in bread. Reproduce by budding. Hydra – found in lakes and ponds. Reproduce by budding. BINARY FISSION occurs when a cell simply grows larger, copies its DNA in genes and chromosomes, and then forms a cell membrane down the midsection of the cell to form 2 new 'daughter' cells. Amoeba reproduces by binary fission. Bacteria reproduces by binary fission. Reproductive System Basics Two Types of Reproduction Sexual: Offspring is produced by combining the genetics of two parents. Multicellular organisms. Requires two parents More genetic variation Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction A single parent cell produces offspring that are exactly like the parent. The new individual has the exact same traits as the parent Two parent cells join together and develop into a new individual Living things make other living things like themselves Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction All organisms must reproduce in order for their kind to survive Most single celled organisms Strawberry Plants; amoebas; coral Human s The new individual shares traits from both parents Most animal s Asexual or Sexual ? Involves two parents. Asexual or Sexual ? Creates Genetically Diverse Offspring Asexual or Sexual ? Creates Genetically Identical Offspring Asexual or Sexual ? Ex: Animals Asexual or Sexual ? Single Celled Organisms Asexual or Sexual ? Involves only one parent. Asexual or Sexual ? Example: Bacteria, Hydra & a Starfish Asexual or Sexual ? Multicellular Organisms CLASSIFYING ORGANISMS • Objective: Classify the following illustrations as either SEXUAL or ASEXUAL organisms. Title: Bacteria Title: Fetus Title: Albino Spider & Alligator ALBINO= lack of normal pigments in the skin that give the organism it’s natural color. It is a genetic abnormality. Title: ANTRHRAX Bacillus Anthrasis Title: A Cat Title: Hungry Lions Title: Wrinkle-Face Bat Title: Budding Yeast Cells Title: Starfish (Regeneration of limb) Title: Monkey Title: Budding Hydra Title: Aye-Aye (From Madagascar) Unique Characteristics= the Aye-Aye has long fingers that tap on the tree branch only to spear it’s prey. It has big ears to detect movement of its prey at night inside the tree. Title: Sharks