* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Blood
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
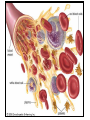
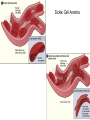
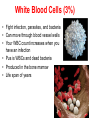
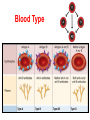
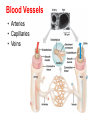
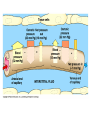
The Blood • How many litres of blood do you have in your body? • 4-6 L • Blood has four main components – Plasma – Red blood cells – White blood cells – Platelets Plasma (55%) • Straw coloured solution containing – Water with dissolved salts (90%) – Plasma proteins (10%) – Nutrients, metabolic wastes, hormones, O2, CO2 • Plasma proteins help transport vitamins and fight viral and bacterial infections Red Blood Cells (41%) • Carry oxygen (hemoglobin) • Produced in bone marrow (2 million/second) • No nuclei – Life span of ~100 days – Gives them a flat disk shape – Increased surface area for O2 molecules – Flexibility to squeeze through different sized blood vessels Sickle Cell Anemia White Blood Cells (3%) • Fight infection, parasites, and bacteria • Can move through blood vessel walls • Your WBC count increases when you have an infection • Pus is WBCs and dead bacteria • Produced in the bone marrow • Life span of years Platelets (1%) • Help with blood clotting • Release clotting factors • Scab forms Blood Type Blood Vessels • Arteries • Capillaries • Veins Arteries: – Carry blood away from the heart to the body tissues – Smaller diameter – High pressure Capillaries: – Exchange of nutrients and wastes (diffusion gradient) – Tiny tubes with large surface area Veins: – – – – Carry blood back to the heart Larger diameter Low pressure Valves allow blood to only flow in one direction