* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Discovery and development of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
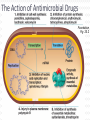
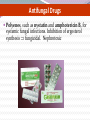
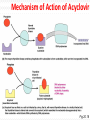
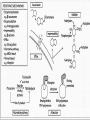
Antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents Antimicrobial Drugs Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to treat a disease. Antimicrobial drugs: Interfere with the growth of microbes within a host. Antibiotic: Of biological origin. Produced by a microbe, inhibits other microbes. Chemotherapeutic agent: synthetic chemicals Today distinction blurred many newer "antibiotics" are biological products that are chemically modified or chemically synthesized Features of Antimicrobial Drugs: Selective Toxicity Cause greater harm to microorganisms than to host Chemotherapeutic index= lowest dose toxic to patient divided by dose typically used for therapy Features of Antimicrobial Drugs Selective toxicity: Drug kills pathogens without damaging the host. Therapeutic index: ratio between toxic dose and therapeutic dose – or ratio of LD50 to ED50 High therapeutic index less toxic Antimicrobial action – Bacteriostatic vs. bactericidal Activity Spectrum – Broad-spectrum vs. narrow- spectrum Tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion – BBB; Unstable in acid; half-life duration The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Foundation Fig 20.2 Inhibition of Protein Synthesis by Antibiotics Figure 20.4 Antifungal Drugs Polyenes, such as nystatin and amphotericin B, for systemic fungal infections. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis fungicidal. Nephrotoxic Antiviral Drugs Nucleoside analogs inhibit DNA synthesis Acyclovir and newer derivatives: Selective inhibition of herpes virus replication. Acyclovir conversion to nucleotide analog only in virus infected cells very little harm to uninfected cells! Fig 20.16 Antiviral drugs Antiviral chemotherapy is still in its infancy. Viruses are more difficult ‘targets’ than bacteria Why ??? Mechanism of Action of Acyclovir Fig 20.16 Antiviral Drugs inhibition of reverse transcriptase at retroviruses such as HIV (e.g.zidovudine) use of complex natural antiviral defences by employing interferon Antibiotic Assays to Guide Chemotherapy Agar Disk Diffusion Method determines susceptibility of an organism to a series of antibiotics: Kirby-Bauer test More sophisticated methods available for clinical labs Drug Resistance Penicillin G resistance of S. aureus from 3% to > 90% Multidrug-resistant S. aureus = MRSA or “super-bug” Vancomycin-resistance Multi drug resistant TB = MDR-TB Evolution of drug resistance: Vertical evolution due to spontaneous mutation Horizontal evolution due to gene transfer ?? Antibiotic Resistance A variety of mutations can lead to antibiotic resistance Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance 1. Enzymatic destruction of drug 2. Prevention of penetration of drug 3. Alteration of drug's target site 4. Rapid ejection of the drug Resistance genes are often on plasmids or transposons that can be transferred between bacteria. Resistance to Antibiotics Fig 20.20 Figure 21.10 Selection of the ATB Requires clinical judgment, detailed knowledge of pharmacological and microbiological factors. Empirical therapy – initial – infecting organism not identified – single broad spectrum agent Definitive therapy- microorganism identified – a narrow –spectrum low toxicity regiment to complete the course of treatment Empirical and Definite Therapy Knowledge of the most likely infecting microorganism and its susceptibility Gram stain Pending isolation and identification of the pathogen Specimen for culture from site of infection should be obtain before initiation of therapy Definite therapy