* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 04-From Cell Division to Tumour - Alexmac
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
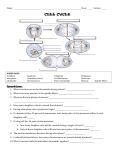
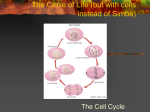
From Cell Division to Tumour Cell Growth • The Cell Grows • New Organelles are made • The DNA Duplicates Cell Growth • The Cell Grows • New Organelles are made • The DNA Duplicates Interphase! The Chromosomes Thicken • The chromosomes thicken. • The chromosomes made up of two chromatids. • Nuclear membrane dissolving. The Chromosomes Thicken • The chromosomes thicken. • The chromosomes made up of two chromatids. • Nuclear membrane dissolving Prophase! Lined-Up • The chromosomes line up in the middle. • Nuclear membrane completely dissolved. Lined-Up • The chromosomes line up in the middle. • Nuclear membrane completely dissolved. Metaphase! Separation • The chromatids separate • Each of the daughter chromatids pulled to opposite sides of the cell. Separation • The chromatids separate • Each of the daughter chromatids pulled to opposite sides of the cell. Anaphase! It’s just a pinch • Chromosomes reach opposite sides • A new nuclear membrane formed around each group of chromosomes • The cell membrane starts to pinch in the middle. It’s just a pinch • Chromosomes reach opposite sides • A new nuclear membrane formed around each group of chromosomes • The cell membrane starts to pinch in the middle. Telophase! And they’re off on their own • The pinching off is complete. • The membrane separates giving rise to two new daughter cells And they’re off on their own • The pinching off is complete. • The membrane separates giving rise to two new daughter cells Cytokinesis ! The Cell Division Story Cell Division on overdrive • Sometimes cell division gets out of hand. • A mass of cells continue to divide without any benefit to the body. • A lump of cells is formed- a Tumour Benign Tumour • A benign tumor does not affect the cells around it. • The surrounding cells maybe crowded and squished, but they continue performing their functions. Malignant Tumour • It interferes with the work of the cells around it. • May destroy the cells around it. • Some malignant tumour cells can break away and travel to other parts of body. Cancer and its Causes • Cancer is a group of diseases that leads to uncontrolled cell division and the formation of a cell lump, a malignant tumour (a malignant tumour cell is said to be cancerous) • Carcinogens- Environmental factors that cause cancer – – – – – – Tobacco smoke X-rays (repeated exposure) Environmental pollution UV radiation (sunlight or tanning beds) Some organic solvents Some chemicals (eg. Bi sphenol A -BPA- in plastic bottles) • Cancer by heredity – The DNA passed from one generation to the next may be damaged. • Cancer by mutation – random changes in DNA. Detection and Diagnosis • Moles: Indicators of Skin Cancer Detection and Diagnosis • X-Rays: can detect cancer in bone, muscles and some organs. Detection and Diagnosis • Mammograms: a type of X-Ray used for breast cancer detection, and regular screening. Detection and diagnosis • Biopsy- A small portion of a suspected tumour is surgically removed, and the cells are compared to normal cells. Differences in size and shape are used to determine if the cells removed are cancerous. Cancer Treatment